Proxim Wireless B11FNFUSB 802.11/b WLAN USB Adapter User Manual Wireless USB Manual
Proxim Wireless Corporation 802.11/b WLAN USB Adapter Wireless USB Manual
User Manual
Wireless USB Adapter
User Manual
Contents
Chapter 1 About the WirelessUSB Adapter.........................3
1-1 Features ...........................................................................................................3
1-2 Applications .....................................................................................................3
1-3 Product Kit ......................................................................................................4
Chapter 2 Network Configuring and Planning...................5
2-1 Network Topology...........................................................................................5
2-2 Roaming ..........................................................................................................6
Chapter 3 Installation ............................................................................7
3-1 System Requirements ......................................................................................7
3-2 Inserting the Wireless Card .............................................................................7
3-3 Installation and Uninstall Process ...................................................................7
Chapter 4 Wireless Utility and Configuration..................13
4-1 Windows 98/2000 Wireless Utility................................................................13
4-2 Windows XP Wireless Utility........................................................................17
Appendix A Troubleshooting....................................................................................23
Appendix B Glossary................................................................................................24
Appendix C Specifications for Wireless Card ..........................................................25
Chapter 1 About the Wireless USB Adapter
This IEEE 802.11b Wireless is compatible with computer USB Adapter. As a
Plug-and-Play device, Windows 95/98/2000/ME/XP will automatically recognize the
wireless USB Adapter and initiate the installation process. Upon successful
installation, the wireless USB Adapter will communicate seamlessly with other IEEE
802.11b wireless products.
1-1 Features
1. Supports up to 11 Mbps data rate.
2. Working range up to 800 ft. in an open environment enhances mobility.
3. Supports point-to-point and point-to-multipoint access provides increased
flexibility.
4. Seamless connectivity to wired Ethernet and PC network LAN’s offers quick,
trouble-free integration with existing networks.
5. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) technology provides secure wireless
connection.
6. Wireless connections eliminate the hassle and cost of cabling.
7. Supports a wide range of LAN (Local Area Network) Network Operating
Systems (NOS)
including Windows 98/2000/NT/ME/XP
8. Easy Plug and Play installation.
9. Omni - directional antenna provides wide range of reception.
10. Greater flexibility to locate or move networked PC’s
1-2 Applications
This wireless USB Adapter offer a fast, reliable, cost-effective solution for wireless
client access to the network. Refer below for examples :
??Remote access to corporate network information
??E-mail, file transfer and terminal emulation
??Difficult-to-wire environments
??Historic or older buildings without Ethernet wiring.
??Buildings with asbestos insulation
??Open areas where wiring is difficult to employ
??Re-layout frequently environments
??Retailers, manufacturers or other organizations that frequently rearrange the
workplace or relocate
??Temporary LANs for special projects or peak time usage
??Trade shows, exhibitions and construction sites that employ temporary
networks.
??Retailers, airline and shipping companies that need additional workstations
for a peak period and auditors that require workgroups at customer sites.
??Access to database for mobile workers
??Medical, technical and retail specialists that require roaming access to a
database or other network resources.
??SOHO (Small Office and Home Office) users
??Perfect for users that need a small, easy-to-install network that deploys
rapidly.
1-3 Product Kit
The wireless USB Adapter includes the following items. Ensure that the items in the
following list have been included. If any of the listed items are missing, please contact
your local dealer.
??One wireless USB Adapter
??One Compact Disk. The CD includes 98/2000/NT/ME/XP driver, utility,
and this user manual
Chapter 2 Network Configuring and Planning
The wireless USB Adapter supports legacy Ethernet LAN network
configuration options as defined by the IEEE 802.11b. The wireless USB Adapter can
be configured as:
. Ad-Hoc mode for no Access Point wireless environment.
. Infrastucture mode for wireless environment with Access Point.
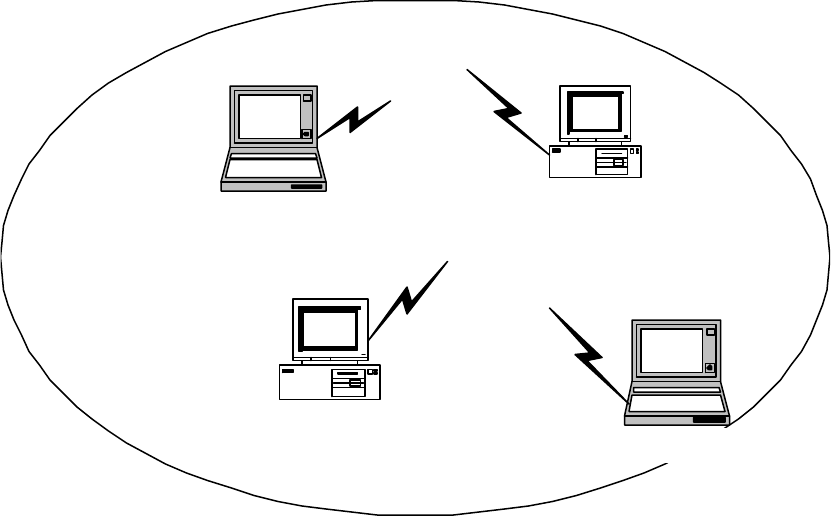
2-1 Network Topology
Ad-Hoc Wireless LAN
Notebook with
T60L198/T60L244
Notebook with
T60L198/T60L244
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
Fig.1 Ad-Hoc Wireless LAN
An Ad-Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers. Each computer is equipped
with a wireless USB Adapter that is configured to the same radio channel in order to
communicate with others. Ad-Hoc wireless LAN configurations are appropriate for
branch level departments or SOHO operations.
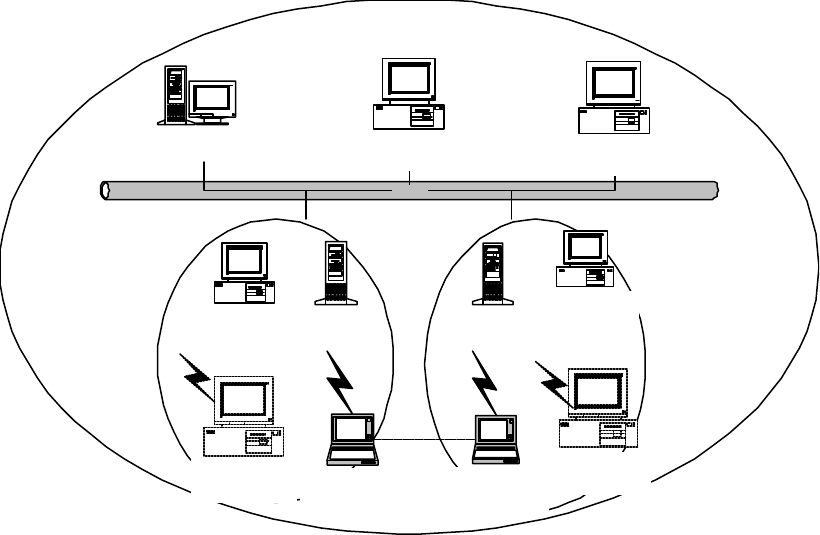
乙太網路
File Server Desktop PC Desktop PC
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
Access Point Access Point
Notebook with
T60L198/T60L244 Notebook with
T60L198/T60L244
Fig.2 Infrastructure Wireless LAN Configuration
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
Desktop PC with
T60L198/T60L244
A group of wireless users and an Access Point compose a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Wireless clients can talk to any computer in both wired and wireless LAN network via
the Access Point.
2-2 Roaming
Infrastructure mode also supports roaming capabilities for mobile users. More
than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS). The continuous
network allows users to roam freely within an ESS. All wireless USB Adapter and
Access Point within one ESS must be configured with the same ESSID in order to
utilize the roaming function. Proper Access Point positioning with a clear radio signal
can greatly enhance wireless performance.

Chapter 3 Installation
3-1 System Requirements
In order to install and use the wireless USB Adapter in your notebook computer, your
notebook system must meet the following requirements:
??USB interface
??CD-ROM Drive
3-2 Inserting the Wireless Card
1. Locate an available USB Adapter.
2. With the USB ADAPTER card pin connector facing the USB ADAPTER slot, you
can easily insert the card into the slot.
3. After properly inserting the wireless card, you can continue with wireless driver
installation.
4. Windows will find the new driver and ask for driver file. You can browse the CD
and select the driver file.
5. Reboot your system and continue to install the wireless utility.
3-3 Installation and Uninstall Process
Install AMBIT Wireless LAN Utility
1. Execute the program setup.exe’ in the CD. Windows displays the dialog similar
to the one below. Press ‘Next’ button to continue.
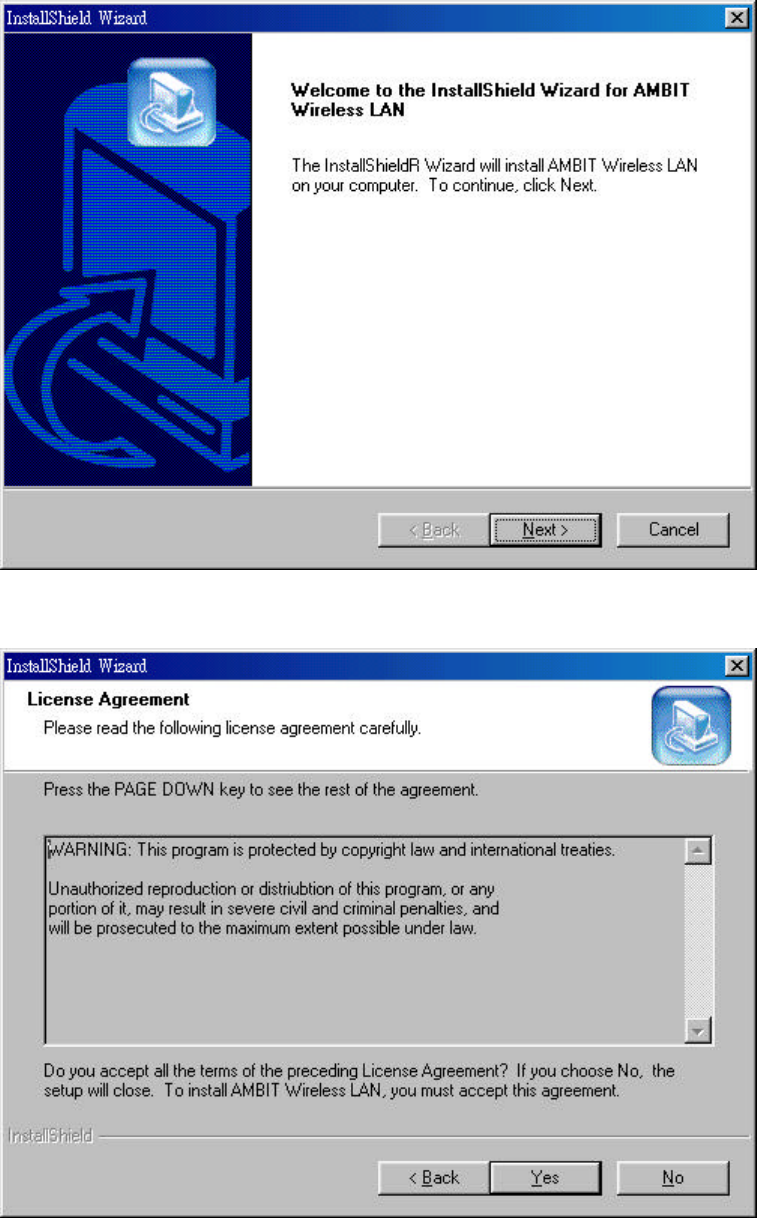
2. It displays a License Agreement dialog. Press ‘Next’ to continue.
3. Select the destination folder that you want to place the files.
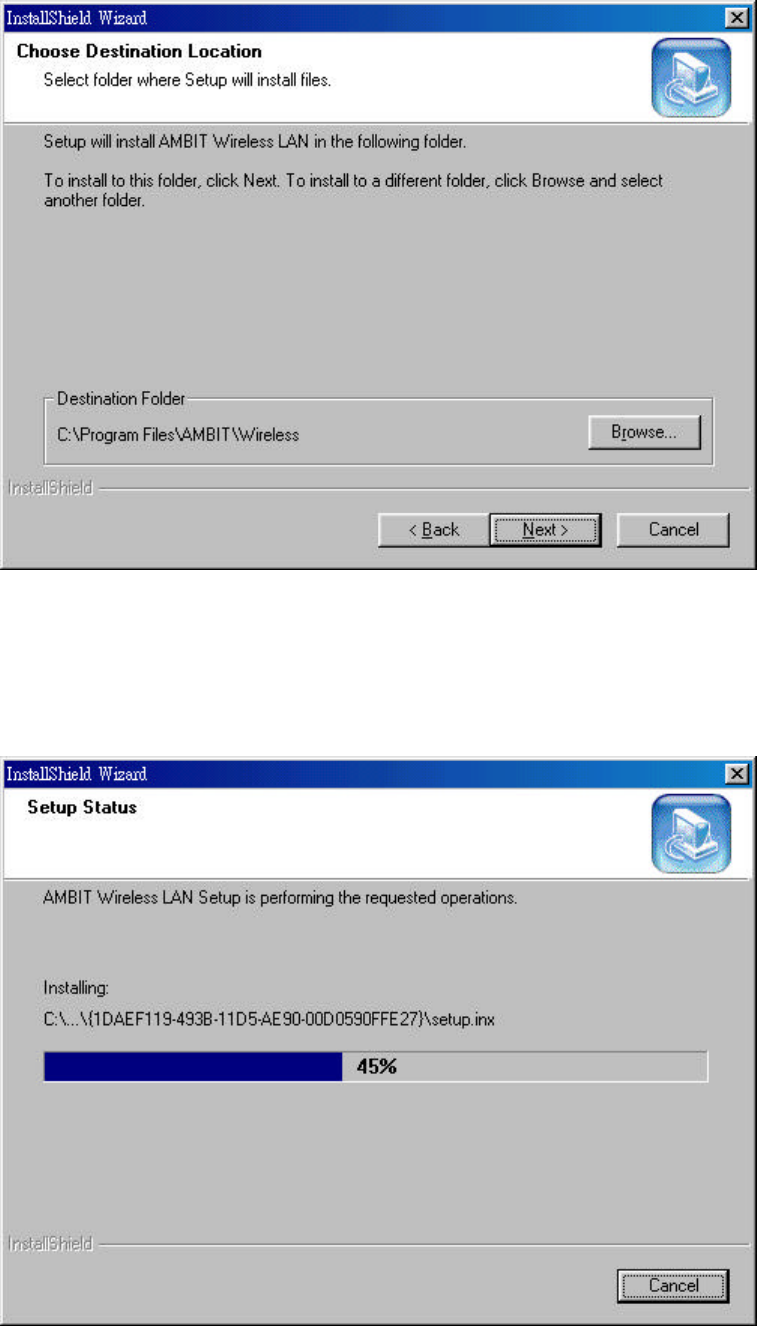
4. Wait for the install program to do the installation.
5. Congratulations! AMBIT Wireless LAN has been installed successfully.
At this moment, Windows will try to find any wireless cards on your system.
This may take a few minutes.
Uninstall AMBIT Wireless LAN
1. One can remove the AMBIT Wireless LAN via the ‘Add/Remove Programs’ in
the ‘Control Panel’. Select ‘AMBIT Wireless LAN’ and click ‘Add/Remove’
button. Windows displays the dialog box similar to the one below.
2. Select ‘Remove’ and then click the ‘Next’ button to perform the un-installation.
Click ‘OK’ button if you really want to remove the AMBIT Wireless LAN.
3. Wait for the un-installation to complete.
4. Click ‘Finish’ to complete the un-Installation.
Chapter 4 Wireless Utility and Configuration
The following sections describe the Wireless Network Configuration Utility.
This utility provides quick access and a friendly user-interface to configure the card
setup.
4-1 Windows 98/2000 Wireless Utility
After installation is completed, a Wireless LAN Utility icon will appear in
Desktop screen. Click it, then you will see the screen below. If you cannot find the
icon, you can select “Start” ->”Programs”->”Wireless LAN Configuration Utility”
Icon.
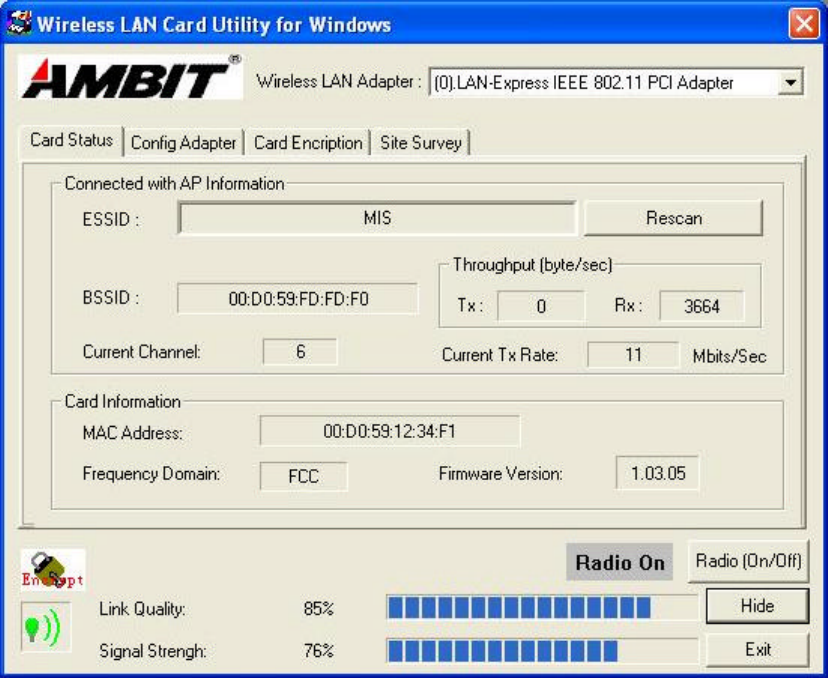
Card Status: You can see the AP information that your card connected. In this page
you also can find Firmware Version and manufacturer information.
ESSID: An acronym for Extended Service Set Identifier, ESSID is the unique name
shared among all clients and Access Points in a wireless network. The ESSID must be
identical for all clients or Access Points participating in the same network. The ESSID
is case sensitive and must not exceed 30 characters. Pressing ‘Rescan,’ will scan all
the APs in the nearby area and choose the strongest one. Using “Link Quality” and
“Signal Strength”, you can determine the wireless transmission quality.
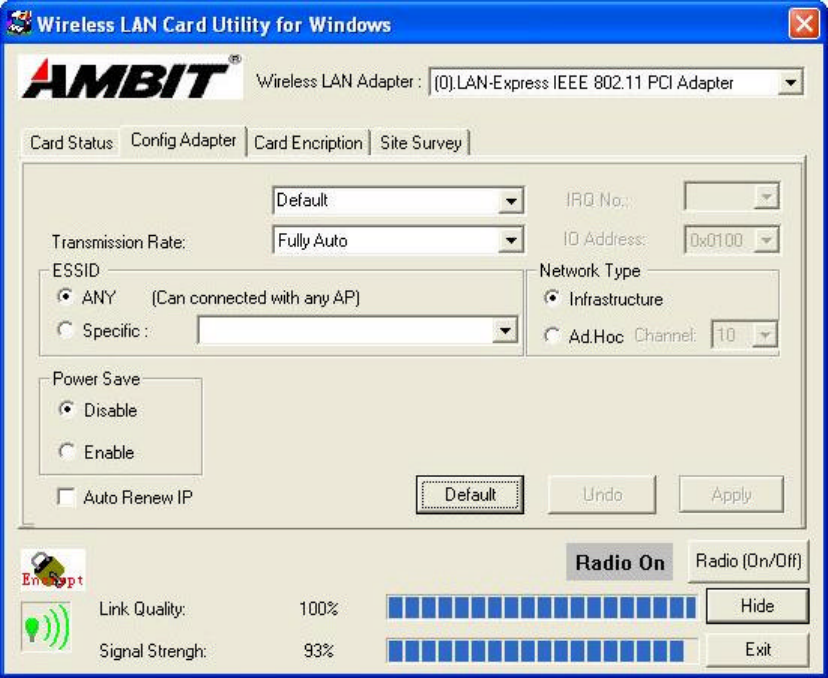
Press ‘Config Adapter’ tab, then you will see the screen below.
There are two network types:
Ad-Hoc: This mode is used for a simple peer-to-peer network. It offers file sharing
between wireless clients without a wireless Access Point (AP).
Infrastructure (Default): This mode allows a wireless LAN to be integrated into an
existing wired network through an AP. Infrastructure type networks also permit
roaming between Access Points while maintaining connection to all network
resources. Infrastructure mode provides additional features, such as WEP security,
power saving and extended range.
ESSID: You can either choose specific AP or connect to any AP in the nearby area.
Power Save: enable it, so it will be triggered when your computer system is inactive.
After computer system active again, wireless connection will rebuild.
Auto Renew IP: Select this item, so the wireless network card can automatically gain
an IP when you move to another network subnet. For example, if you are in
192.168.1.X subnet and move to 192.178.5.X subnet, your computer will renew an IP
address from 192.178.5.X subnet.
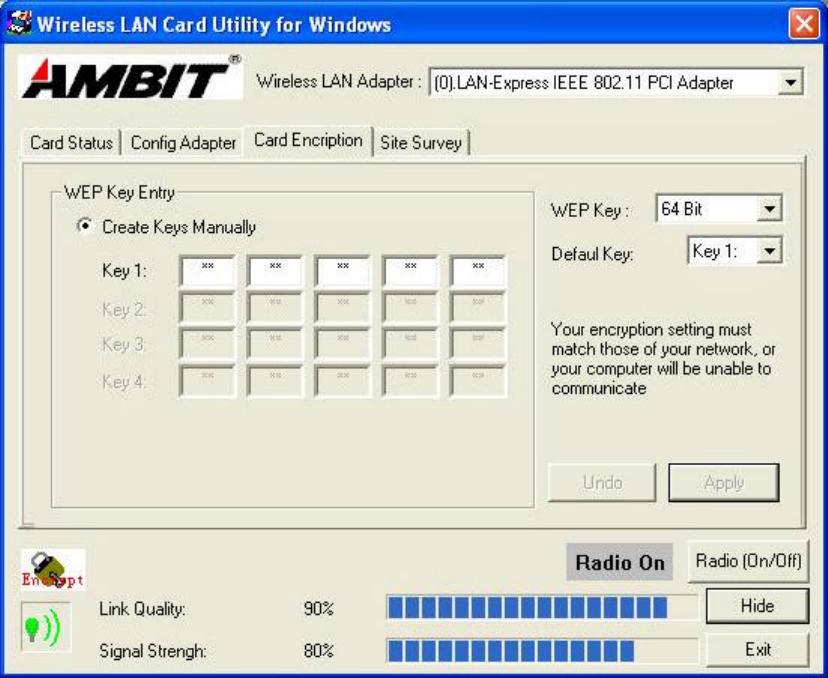
Press ‘Card Encryption’ tab, then you will see the screen below.
Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP is an encryption scheme used to protect your
wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64-bit keys,128-bit keys
to provide data encryption for your wireless network. AP and wireless card should use
the same WEP key in order to communicate
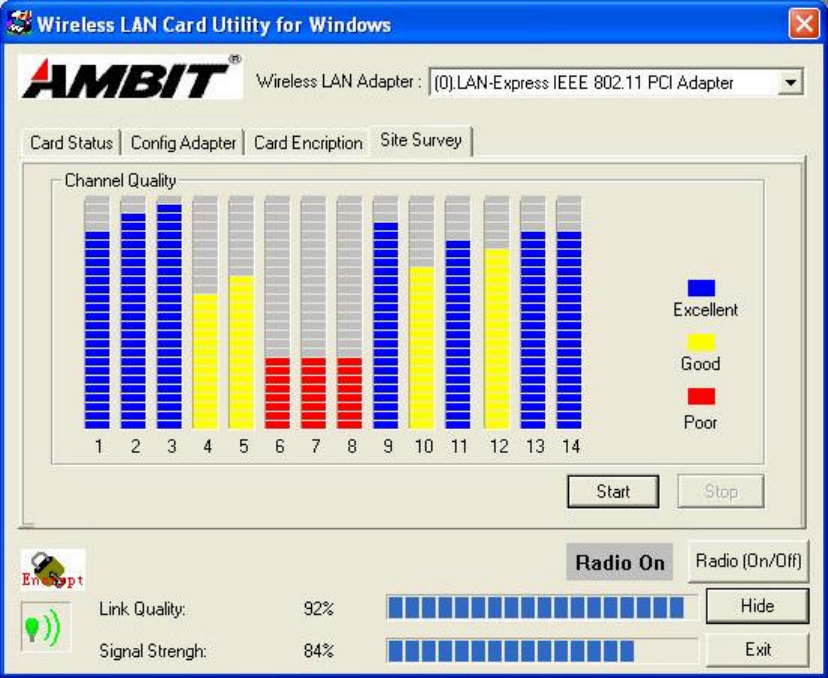
Use the Site Survey Tool. You can identify each channel transmission quality.
4-2 Windows XP Wireless Utility
NOTE: You do not need to install the utility from the CD if you are using Windows
XP. Windows XP provides wireless Utility as below.
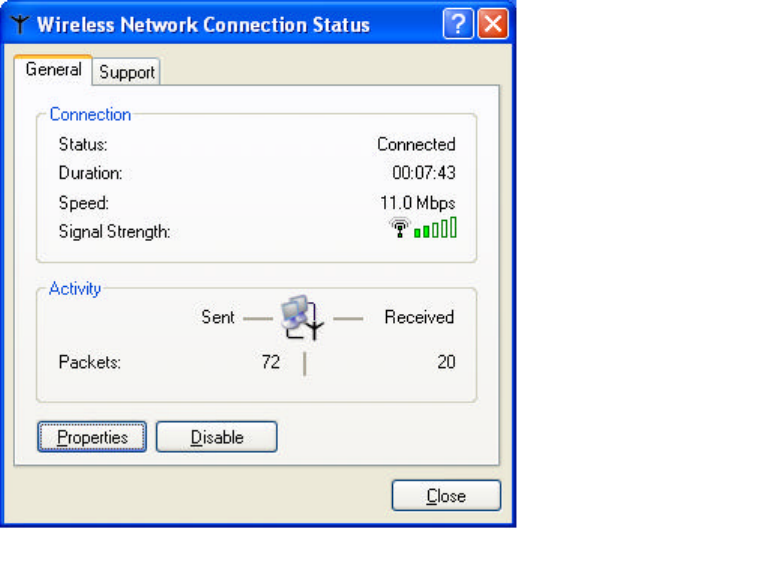
1. To configure the wireless card setting, you can select Start\Settings\Network
Connection in the Windows XP. Choose the wireless network connection, then
you will see below screen. From this screen, you can see wireless connection
status and wireless signal level.
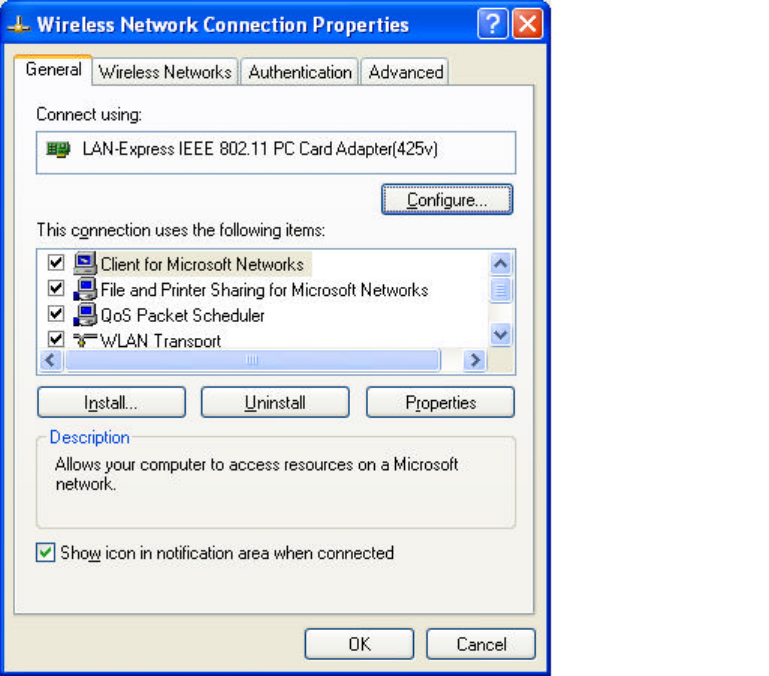
2. Select ‘Properties’ in the above screen. The following windows will show up.
In ‘General’ page, wireless card information and networking protocol have been
displayed. Extra networking protocol can be installed in this page.
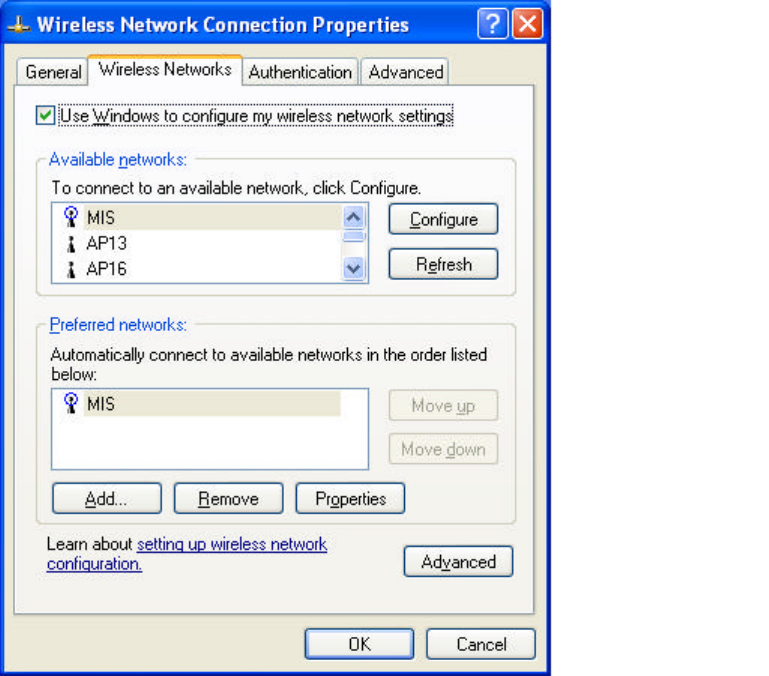
3. Select Wireless Networks page, you can see available wireless networks in your
nearby area. You can add your preferred wireless Access Point to your list, so your
wireless card will search for specific wireless networks.
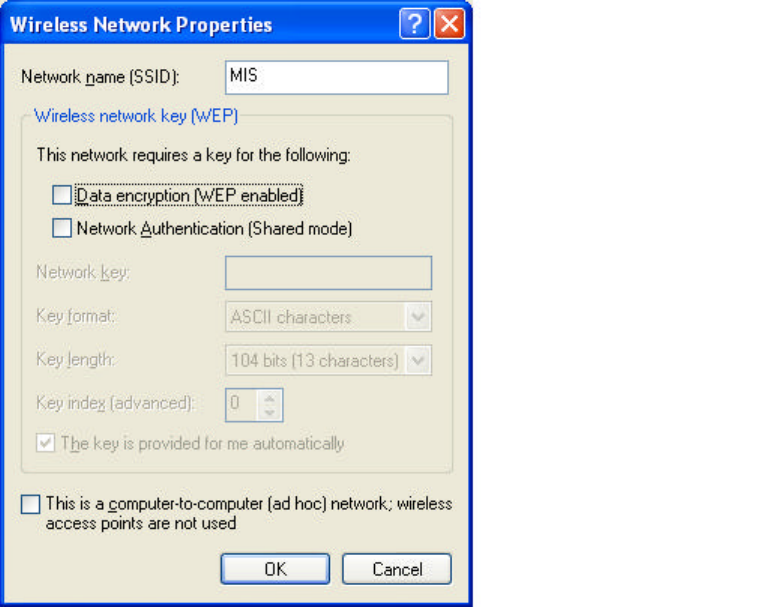
3. Click ‘Configure’ above to setup wireless security and data encryption.
Define your network name (SSID) in the following windows, so your can join a
specific wireless network. Check AP has WEP on or not. You wireless network will
need to have same WEP setting with AP in order to communicate. If your wireless
network don’t have any AP, mark the ‘This is computer-to computer (ad-hoc) network;
wireless access points are not used’
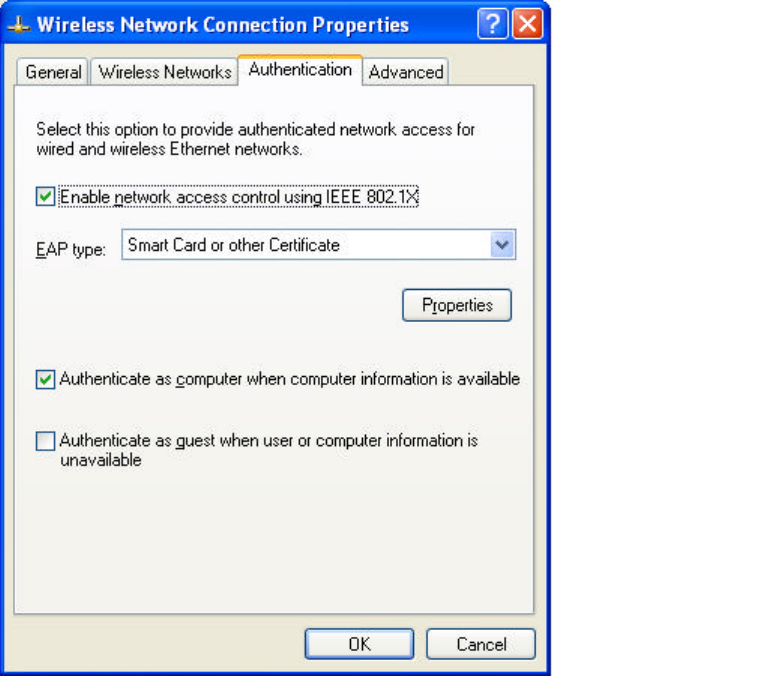
This window provides authentication via 802.1X. 802.1X, an IEEE standard that
provides an authentication framework for 802-based LANs. 802.1X takes advantage
of an existing authentication protocol known as the Extensible Authentication
Protocol. 802.1x, giving someone secure, encrypted, wireless access on a Microsoft
network will be as easy as setting a flag on the users domain account.
What does this mean for the Home Network user?
802.1x will ensure that if and when you make the change over to Wireless Ethernet,
your neighbor will not be able to access your wireless LAN!
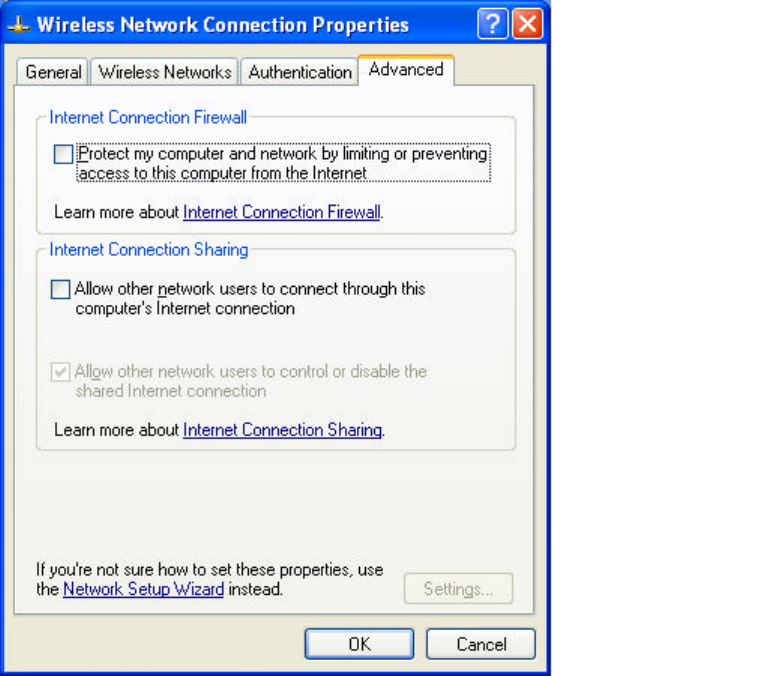
The ‘Advanced’ window offers Firewall and Internet Connection Sharing functions.
Depending on your networking environment, you can select the functions below.
Appendix A Troubleshooting
Problem Solving
1. My computer does not recognize the wireless network card.
Solution:
??The wireless network card is not properly inserted into the USB Adapter slot.
??Ensure that the wireless network card has been inserted into an available USB
Adapter .
2. The wireless network card does not work properly.
Solution:
??Insert the USB Adapter into Notebook’s slot again. A beep should be heard if the
card properly inserted.
??The Activity LED indicator is active if the card is properly connected.
??Right click on “My Computer” and the select Properties. Select the device
Manager and click on the Network Adapter. You will find “LAN-Express IEEE
802.11 USB Adapter” if it is installed successfully. If you see the Yellow
Question Mark besides the wireless network card, then the wireless card is not
properly installed. Please check below:
?? Check if your Notebook has a free IRQ
?? Check that you have inserted the right card and have installed the proper
driver.
?? Try to remove driver, install again, and then reboot your computer.
??Confirm the station is configured the same ESSID as the same wireless network.
??Check your channel is the same as AP setting. Try to use ‘Rescan’ function in
the card status page after launch Wireless Utility.
Appendix B Glossary
Access Point - An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and
wireless networks together.
Ad-Hoc - Ad-Hoc is a peer- to-peer wireless network without Access Point. A group
of wireless clients consistent an independent wireless LAN.
Backbone - The core infrastructure of a network, the portion of the network that
transports information from one central location to another central location. The
information is then off-loaded onto a local system.
BSS - Stands for “Basic Service Set.” An Access Point associated with several
wireless stations.
ESS - Stands for “Extended Service Set.” More than one BSS can be configured as an
Extended Service Set. An ESS is basically a roaming domain.
Ethernet - A popular local area data communications network, originally developed
by Xerox Corp., which accepts transmission from computers and terminals. Ethernet
operates on 10/100 Mbps transmission rate over shielded coaxial cable or over
shielded twisted pair telephone wire.
Infrastructure - An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure
configuration.
USB ADAPTER - Personal Computer Memory Card International Association,
which develops standards for PC cards, formerly known as USB Adapter, are
available in three “types” which are about the same length and width as credit cards,
but range in thickness from 3.3 mm (Type I) to 5.0 mm (Type II) to 10.5 mm (Type
III). These cards can be used for many functions, including memory storage, as
landline modems and as wireless LAN.
Roaming - A function that allows one to travel with a mobile end system (wireless
LAN mobile station, for example) through the territory of a domain (an ESS, for
example) while continuously connecting to the infrastructure.
Appendix C Specifications for Wireless Card
??Frequency Band: 2400 ~ 2483.5MHz (for US, Canada, and ETSI)
2400 ~ 2497MHz (for Japan)
??Modulation TYPE: CCK, BPSK, QPSK
??Operating Channels:
11 channels (US, Canada)
13 channels (ETSI)
14 channels (Japan)
??Radio Technology: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
??Data Rate: 1 / 2 / 5.5 / 11 Mbps
??Output Power: > +13dBm
??Receive sensitivity: Min. -76dBm for 11Mbps; Min. -80dBm for 5.5/2/1
Mbps ;(@BER 10E-5)
??Antenna Type: Printed antenna
??Power Consumption : TX mode 350 m A (Max.) ; Rx mode 230
m A (Max.);
??Package: USB Adapter
??Certification: FCC Part 15
ETSI 300.328
ARIB STD33 & T66
??Driver : Windows 98/2000/ME/NT/XP

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Caution:. Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
RF Exposure Warning: This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device is provided with an internal antenna and minimum 20 cm
spacing must be maintained between this PC C Card and all person’s body (excluding extremities of
hands, wrist and feet) during wireless mode of operation. Further, this transmitter must not be co-
located or operated in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.