Askey Computer WLC0010 PCMCIA Card User Manual WLC0010 Manual
Askey Computer Corp PCMCIA Card WLC0010 Manual
User manual

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card
User’s Manual
2002 All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any
form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written
permission of the seller.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The material contained
herein is supplied without representation or warranty of any kind. The seller therefore assumes
no responsibility and shall have no liability of any kind arising from the supply or use of this
document or the material contained herein.
Trademarks
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other
trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
Rev: 01
April 2003

I
Contents
About This Manual....................................................................................................................................................... IV
Chapter 1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................... 1
Wireless LAN Basics................................................................................................................................................... 2
Local Area Network (LAN)........................................................................................................................................................2
Ad-Hoc Mode ............................................................................................................................................................................3
Infrastructure Mode ..................................................................................................................................................................4
Roaming ....................................................................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 2 Installing the Wireless LAN Card............................................................................................................ 7
System Requirements................................................................................................................................................. 8
Installing Wireless LAN Driver and Software .............................................................................................................. 9
Part 1: Installing Driver ...........................................................................................................................................................9
Part 2: Installing Software ......................................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility .................................................................................................................... 15
Accessing Vendor’s Wireless LAN Utility.................................................................................................................. 16
Notice When Assessing Wireless LAN Utility under Windows XP ..........................................................................................18
Configuration............................................................................................................................................................. 20

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
II
Available Wireless Networks...................................................................................................................................................20
Available Profiles....................................................................................................................................................................22
WEP Settings...........................................................................................................................................................................23
Advanced Configuration............................................................................................................................................ 26
Status ........................................................................................................................................................................ 27
Statistics .................................................................................................................................................................... 28
About ......................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility ............................................................................... 31
Connecting to an Access Point or Wireless LAN Card ............................................................................................. 31
Viewing Wireless Connection Status ........................................................................................................................ 34
Configuring Your Wireless Properties....................................................................................................................... 35
Chapter 6 Uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card..................................................................................................... 41
Uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card Software........................................................................................................... 41
Removing the Wireless LAN Card (For CardBus Adapter)....................................................................................... 44
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................................... 45
Appendix A Limited Warranty................................................................................................................................. 49
Wireless LAN Hardware............................................................................................................................................ 49
Wireless LAN Software ............................................................................................................................................. 50
Appendix B Setting Up TCP/IP................................................................................................................................51
For Windows 98/ME.................................................................................................................................................. 51

Contents
III
For Windows 2000/XP .............................................................................................................................................. 54
Glossary....................................................................................................................................................................... 57

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
IV
About This Manual
This manual was written for the following type of wireless adapter:
• 32-bit CardBus Adapter
For brevity, throughout this manual Wireless LAN Card is used to indicate all the types. Also,
the following terms/abbreviations are used interchangeably:
• Access Point – AP
• Peer-to-Peer – Ad Hoc
• Wireless LAN – WLAN
• Ethernet network – LAN – network
This User’s Manual contains information on how to install and configure your Wireless LAN
Card. From now on, we will guide you through the correct configuration steps to get your
device up and run.
1
Chapter 1 Introduction
This Wireless LAN Card is an IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN PCMCIA/USB adapter. It allows
your computer to connect to a wireless network and to share resources, such as files or printers
without being bound to the network wires. Operating in 2.4GHz Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum (DSSS) radio transmission, the Wireless LAN Card transfers data at speeds up to
11Mbps. Both Ad-Hoc and Infrastructure mode are supported. For network security concern,
64/128-bit Wired Equivalent Protection (WEP) algorithm is used. In addition, its standard
compliance ensures that it can communicate with any 802.11b networks.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
2
Wireless LAN Basics
This section contains some Wireless LAN basics to help you better understand how the
product work together to create a wireless network.
Local Area Network (LAN)
Simply put, a LAN is a network that exists in a relatively limited area. A network is two or
more computers connected together sharing files and peripheral devices such as printers.
The Wireless LAN Card allows you to interact with other computers without having to run
cables normally associated with networks. This lets you move your computer around while
staying connected to your network.
There are two ways to use the Wireless LAN Card. One way is to connect directly to one or
more Wireless LAN Card equipped computers, forming an Ad-Hoc wireless network. The
second way is to connect to an Access Point that gives you access to an existing wired LAN,
forming an Infrastructure wireless network.
Chapter 1 Introduction
3
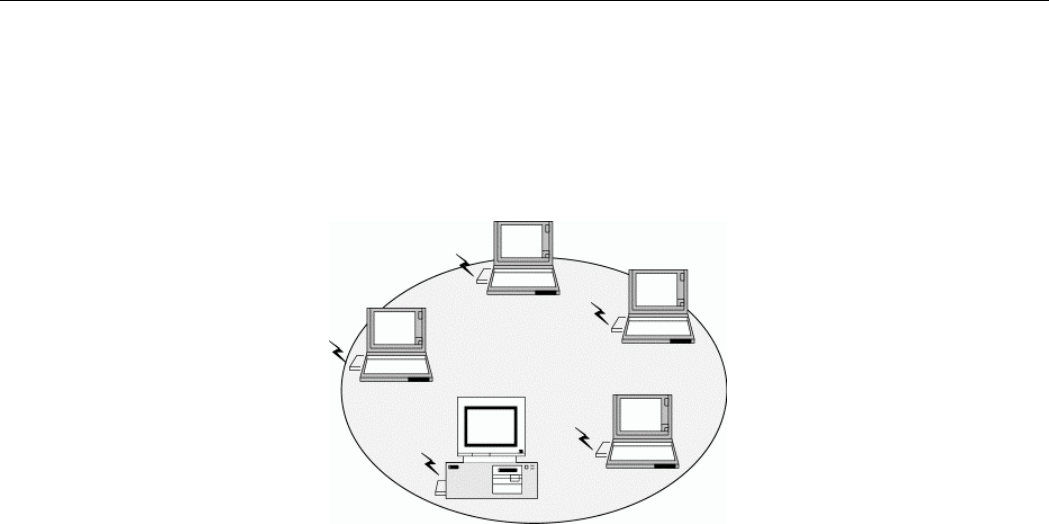
Ad-Hoc Mode
The Ad-Hoc Group offers peer-to-peer connections between workstations, allowing
communication between computers within range that have a Wireless LAN Card installed. A
wireless Ad-Hoc network can also access a wired LAN’s TCP/IP service (such as e-mail and
the Internet) by using a TCP/IP software router on an Ethernet equipped PowerBook or
notebook.
Figure 1-1 Ad-Hoc Mode
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
4
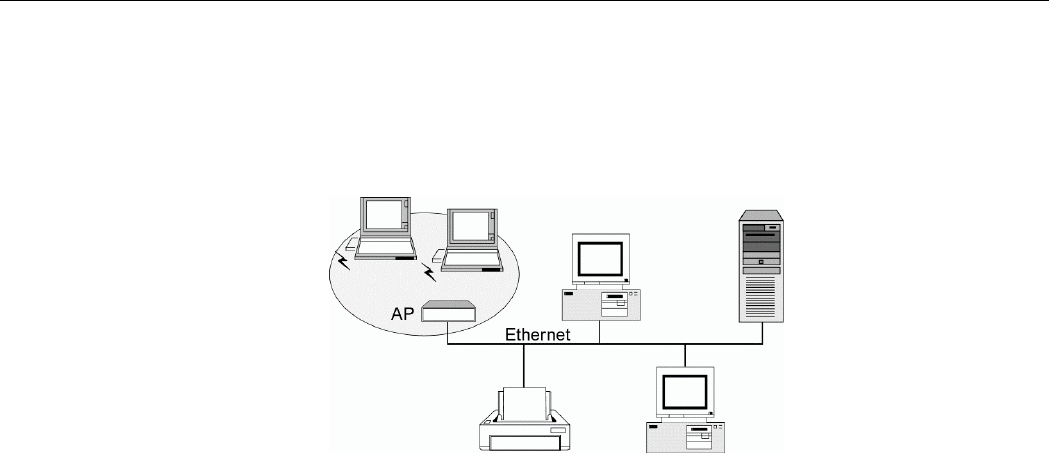
Infrastructure Mode
The Infrastructure network uses an AP or several APs as a gateway, linking the wireless
network to a wired LAN. As a result, portable workstations or desktops on your wireless
network have access to all of the features of your wired LAN including e-mail, Internet access,
network printers and file server.
Figure 1-2 Infrastructure Mode
Chapter 1 Introduction
5
Roaming
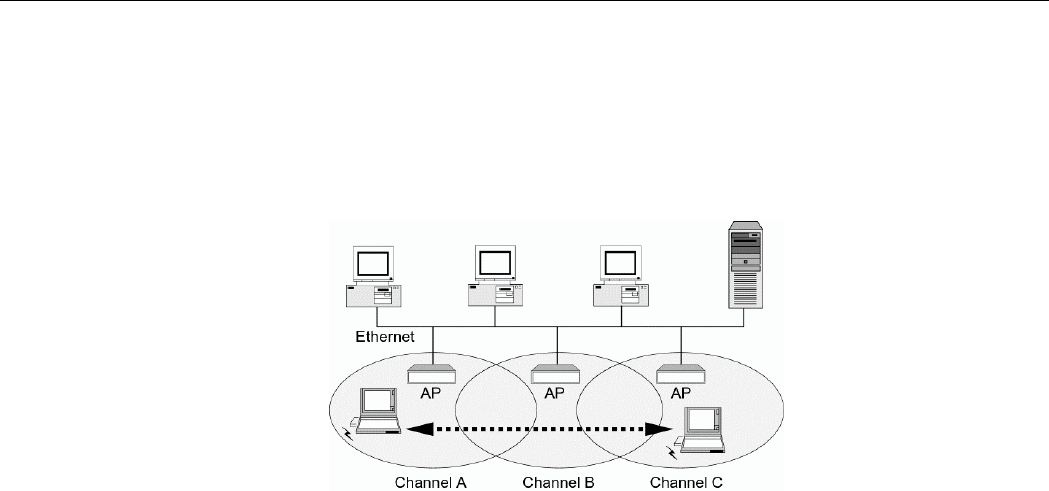
Multiple Access Points can be installed to extend the wireless service coverage area for
seamless wireless access. Within an extended service area, all Access Points and wireless
clients must have the same Service Set Identity (SSID). Roaming among different Access
Points is controlled automatically to maintain the wireless connectivity at all times.
Figure 1-3 Roaming Across Multiple Access Points

7
Chapter 2 Installing the Wireless LAN Card
This chapter describes the installation process of the driver and software for the Wireless LAN
Card. Proper driver installation is to allow the device to operate on your host computer while
the utility software, Wireless LAN Utility, is to help you configure and monitor your Wireless
LAN Card.
In case you need to install the driver and software for any reason, follow the instructions
described in this chapter.
Note: The installation procedures are basically the same in Windows operating system. The
following description uses Windows XP as the example environment.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
8
System Requirements
To use the Wireless LAN Card, your computer must meet the following minimum
requirements:
z Pentium-class PC, 300MHz or better recommended
z 64 MB of RAM, additional memory recommended
z Hard disk space at least 30 Mbytes
z Windows 98(SE)/Me/2000/XP
z UL listed I.T.E. computers
z For CardBus wireless adapter: 32-bit Cardbus expansion slot
Chapter 2 Installing the Wireless LAN Card
9
Installing Wireless LAN Driver and Software
Part 1: Installing Driver
Follow these steps to install the Wireless LAN Card driver and software.
1. Close all Windows programs that are running and insert the provided Software Utility
CD into your CD-ROM drive
2. Insert your wireless adapter into the PCMCIA slot of your computer. The Windows
Plug-and-Play feature will detect the new device.
3. Select Install from a list or specific location (Advance) and click Next.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
10
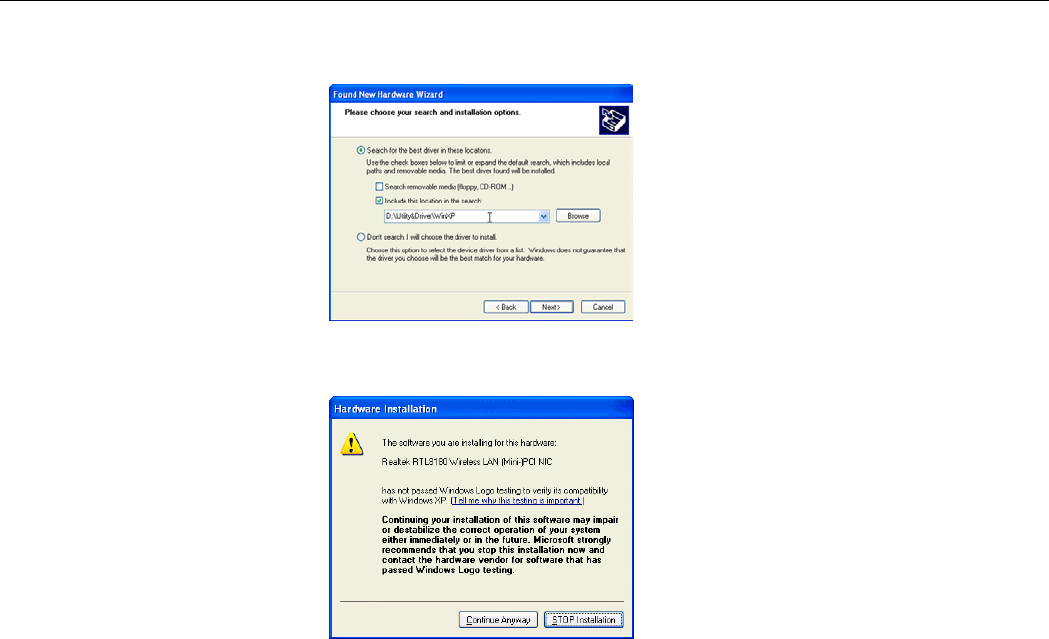
4. With Include this location … selected, click Browse to locate the driver from
D:\Utility&Driver of the Software Utility CD where D is the drive letter.
5. If Windows logo compatibility message appears, click Continue Anyway to proceed
with the installation.
Chapter 2 Installing the Wireless LAN Card
11
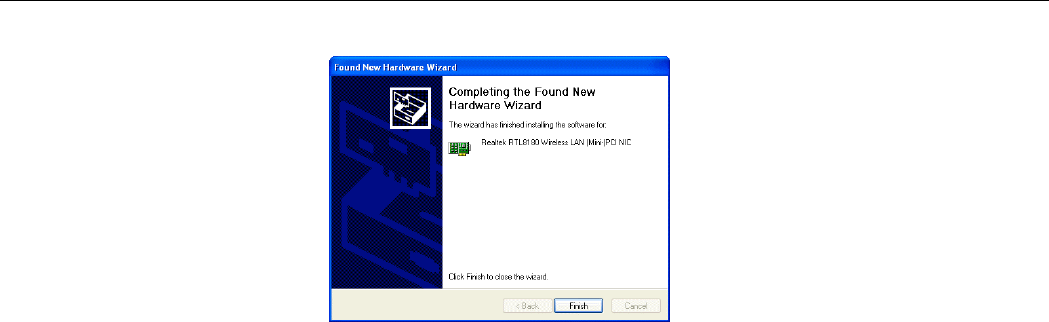
6. Click Finish.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
12
Part 2: Installing Software
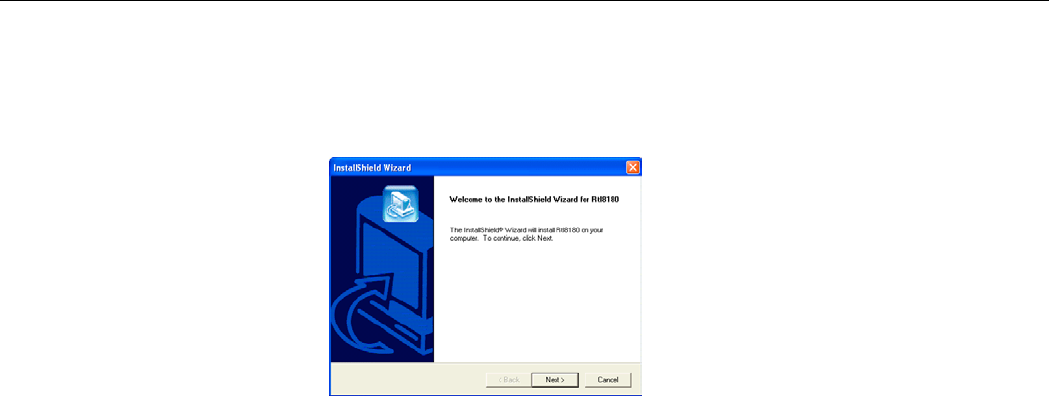
1. Run Setup.exe from D:\Utility&Driver folder of the Software Utility CD where D is the
drive letter. When the welcome screen pops up, click Next.
Chapter 2 Installing the Wireless LAN Card
13
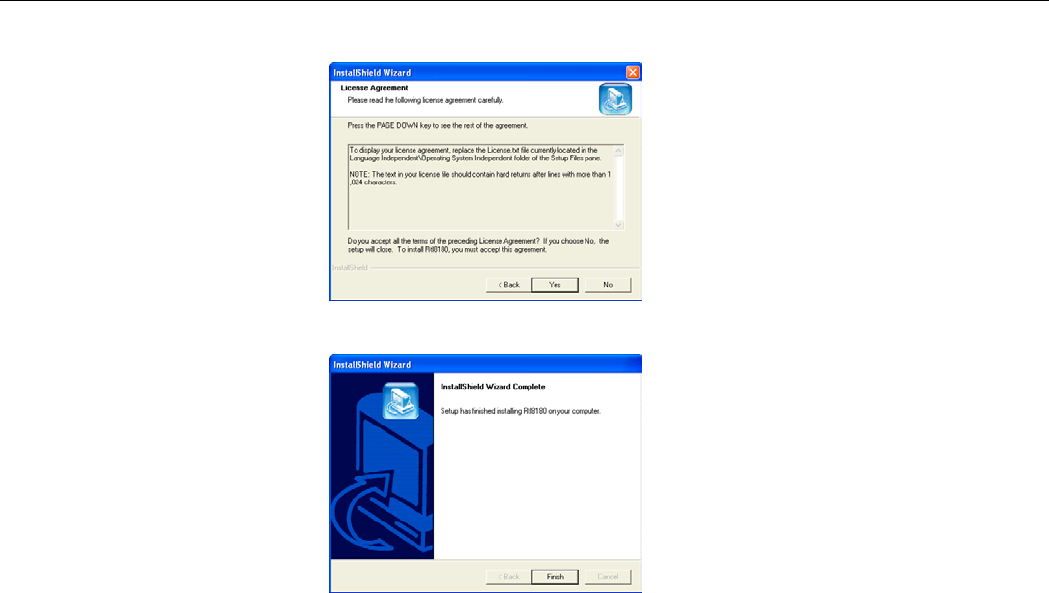
2. When the License Agreement screen appears, click Yes.
3. Click Finish when the following screen appears.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
14
Note: If you need to set up the TCP/IP address or the subnet mask, refer to “Appendix B
Setting Up TCP/IP” for details.
15
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
Once your wireless adapter driver and software is properly installed, the provided Wireless
LAN Utility is ready for use. You should be able to find the wireless icon on your system tray.
See the ensuing subsections for instructions on using the vendor-provided wireless utility.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
16
Accessing Vendor’s Wireless LAN Utility
To access vendor-provided Wireless LAN Utility:
1. Double-click the wireless icon on the system tray.
2. Click the Advanced button.
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
17
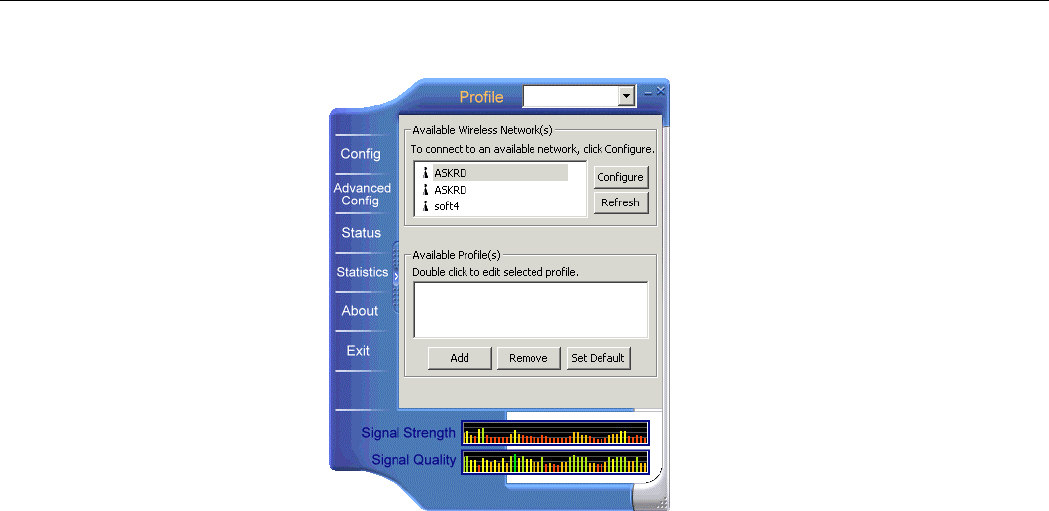
3. The vendor-provided utility is launched. You may click the menu on the left to execute
corresponding tasks.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
18
Notice When Assessing Wireless LAN Utility under Windows XP
Aside from using the vendor’s WLAN utility for configuration, Windows XP includes a
Wireless Zero Configuration Utility for you to configure your wireless adapter. By default,
your wireless adapter is managed by Windows XP-included wireless utility. Under this
circumstance, you will be prompted with the “You are in “Windows Config” mode” message
if you try to access vendor-provided utility by double-clicking vendor’s wireless icon in the
system tray.
You can choose to configure your wireless network via either the vendor’s Wireless LAN
Utility or Windows XP-included wireless utility.
Using Vendor’s Wireless LAN Utility
To use the vendor’s WLAN utility for configuration purposes, you should disable the
Windows XP-included wireless utility by these steps:
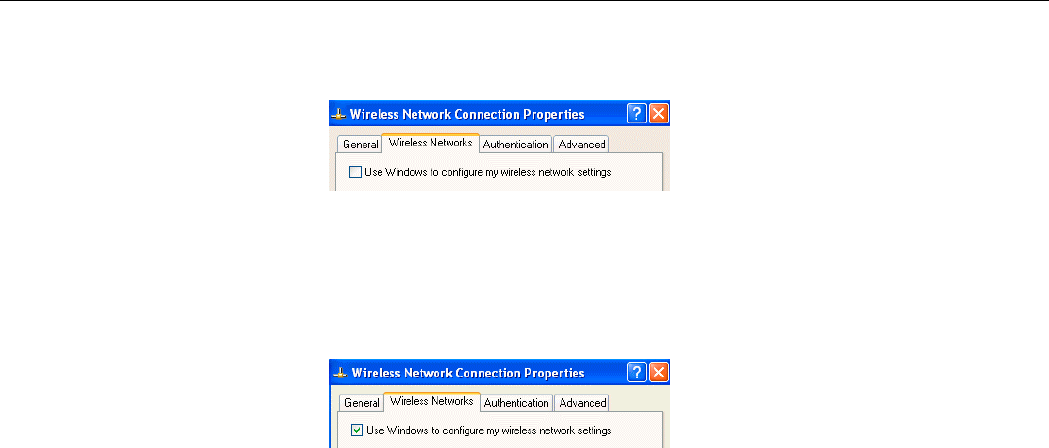
4. Double-click the Windows XP wireless tray icon and then click Properties (or
Advanced). Then select Wireless Networks tab.
Vendor’s wireless icon
Windows XP wireless icon
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
19
2. On the Wireless Networks tab, uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings box and click OK. This will restore the Wireless Networks tab in
wireless LAN utility.
Reverting back to Windows XP-included Wireless Utility
Double-click the Windows wireless icon (not the vendor’s WLAN utility icon) and then click
Advanced (or Properties). Click the Wireless Networks tab and check the Use Windows to
configure my wireless network settings box and click OK.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
20
Configuration
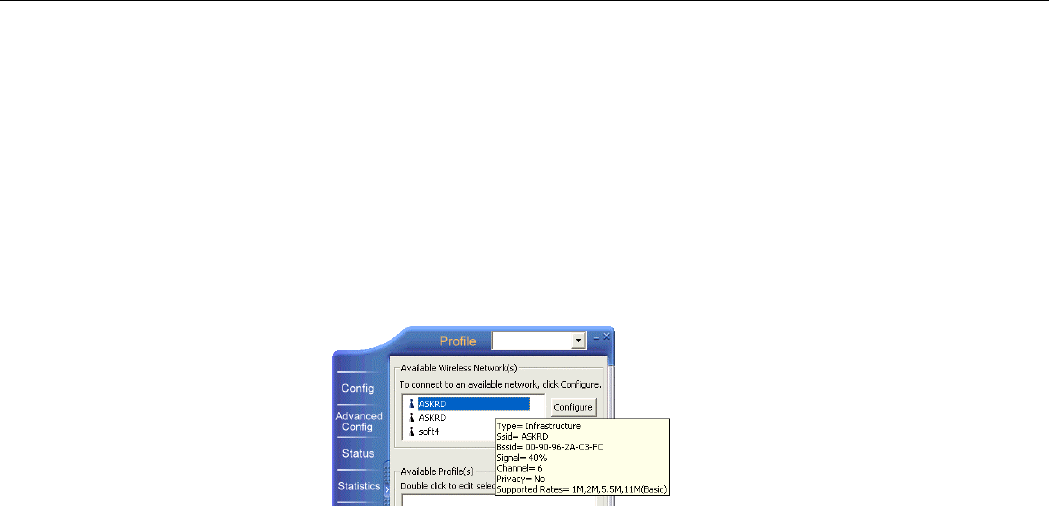
The Config screen comprises two sections: Available Wireless Networks and Available
Profiles.
Available Wireless Networks
The utility automatically searches and displays available “open” wireless networks in this list.
Highlighting a network will pop up the related parameters used by the network.
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
21
If you select a network and click Configure, you can configure the WEP and 802.1x settings.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
22
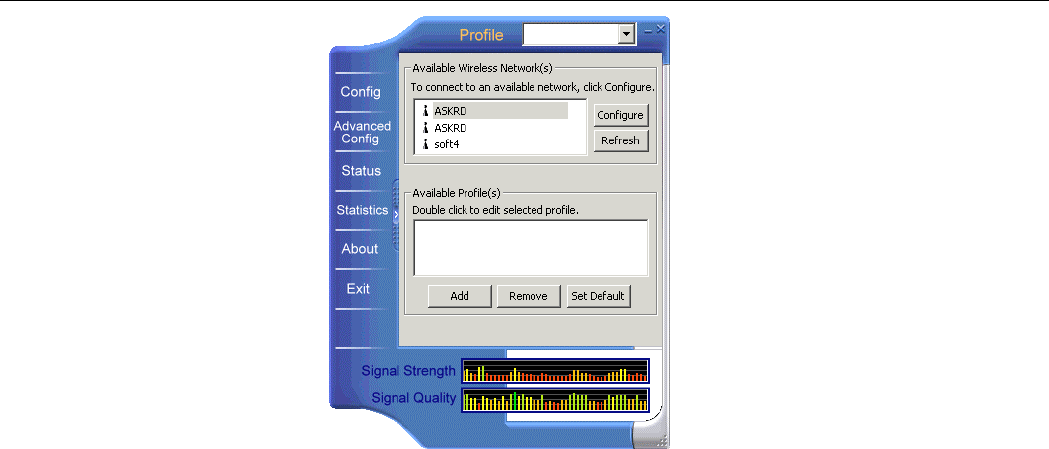
Available Profiles
This section allows you to add, edit and remove a profile.
To add a new profile, click Add and then set up these parameters:
Screen Item Description
SSID Specifies the name of the WLAN group you want to participate in.
For Ad Hoc mode: A network name is mandatory. The SSID for
all stations in a single Ad Hoc network must be same.
For Infrastructure mode: If using the special SSID “any”, your
Wireless LAN Card will connect to the first compatible and “open”
AP with the best signal strength within the connection range.
WEP Specifies whether to enable WEP settings. See next section for more
information.
802.1x Do not check the “Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication for this
network” option unless you are going to join a 802.1x-enabled
wireless network.
Operating Mode To join an Ad-Hoc network, check the “This is a computer-to-
computer (ad-hoc) network…” check box.

Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
23
Screen Item Description
To join an Infrastructure network where an AP is required, leave the
“This is a computer-to-computer (ad-hoc) network…” check box
unchecked.
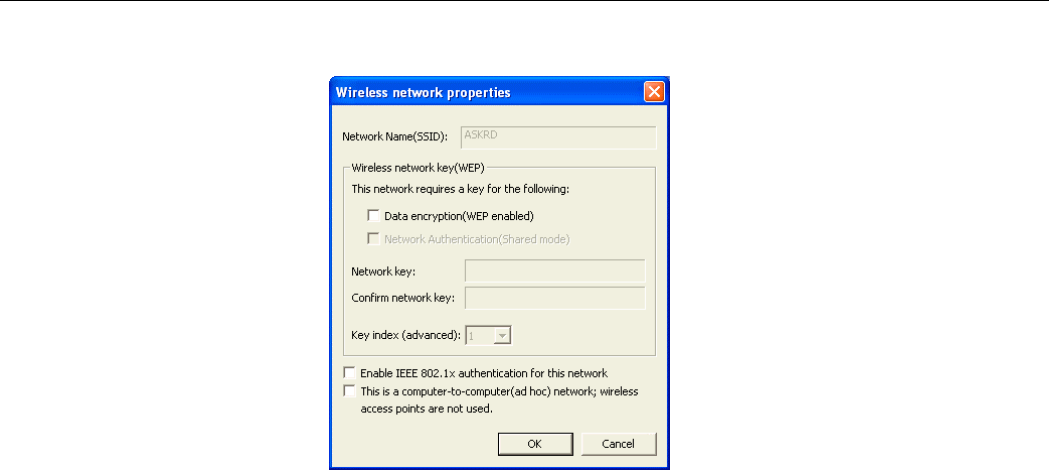
WEP Settings
In the WEP section you may take additional measures to secure your network by using WEP
(Wired Equivalent Privacy). If encryption is not necessary, just leave the Data
encryption(WEP enabled) check box empty. To enable WEP, take the steps below:
1. Check the Data encryption (WEP enabled) check box.
2. In the Network Authentication (Shared Mode) item, select this check box to use
Shared Key or leave it empty to use Open Key. You should use the same authentication
method as used by your targeted wireless network.
• Open Key: If your targeted wireless network uses Open Key, your authentication
request will be always accepted regardless of your WEP keys. You are allowed to
join the network assuming that your SSID matches the SSID of the targeted
wireless network.
• Shared Key: If your targeted wireless network uses Shared Key, your wireless
adapter must be set to use correct WEP to pass the authentication. If selected, your
wireless adapter must use identical WEP keys as the targeted wireless network.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
24
3. In the Network key and Confirm network key fields, enter 40bits or 104bits WEP keys
in hexadecimal format. Note that the WEP keys must be the same as your target wireless
network.
When using Hexadecimal format, only digits 0-9 and letters a-f, A-F are allowed. Make
sure to enter the character matching the required key format and length as below:
Hexadecimal digits
40 bits 10 hexadecimal digits
104 bits 26 hexadecimal digits
4. In the Key index (advanced) field, select an index for the key you entered.
After finishing all required settings, click OK. You will return to the Config screen and found
the new profile named after the SSID you entered in the Available Profiles list.
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
25

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
26
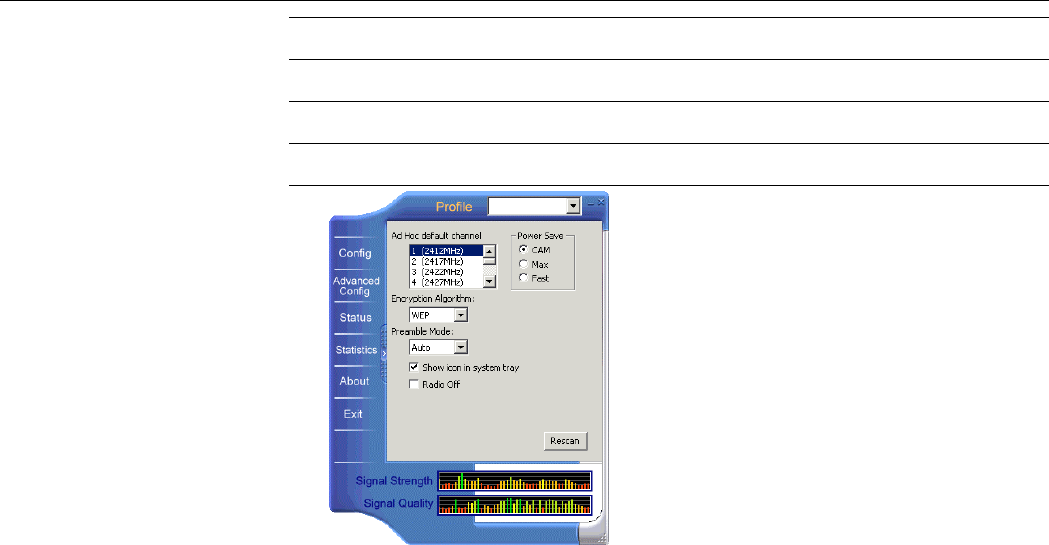
Advanced Configuration
The following table lists the parameters on this screen:
Screen Item Description
Ad Hoc default channel This setting determines which channel is to be used if your wireless
adapter is the first to start an Ad Hoc network.
When selecting a channel, make sure to select a legal channel
according to your frequency domain.
Encryption Specifies the encryption as WEP, TKIP or AES.
Preamble Mode The preamble is part of the IEEE 802.11b physical layer
specification. All 802.11b devices are mandatory to support the
long preamble format, but may optionally support the short
preamble. This Wireless LAN Card supports the short preamble.
The Short option allows to communicate with other 802.11b
devices which support short preamble to boost the throughput. The
Long option is typically used in a “noisy” network. Make sure to
use the appropriate preamble type according to your network
environment.
Show icon in system
tray Specifies whether to show wireless icon in the system tray.
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
27
Screen Item Description
Radio Off Allows to disable/enable RF signal.
Power Save Specifies the power save mode to be used.
Rescan Allows to rescan the current associated network.
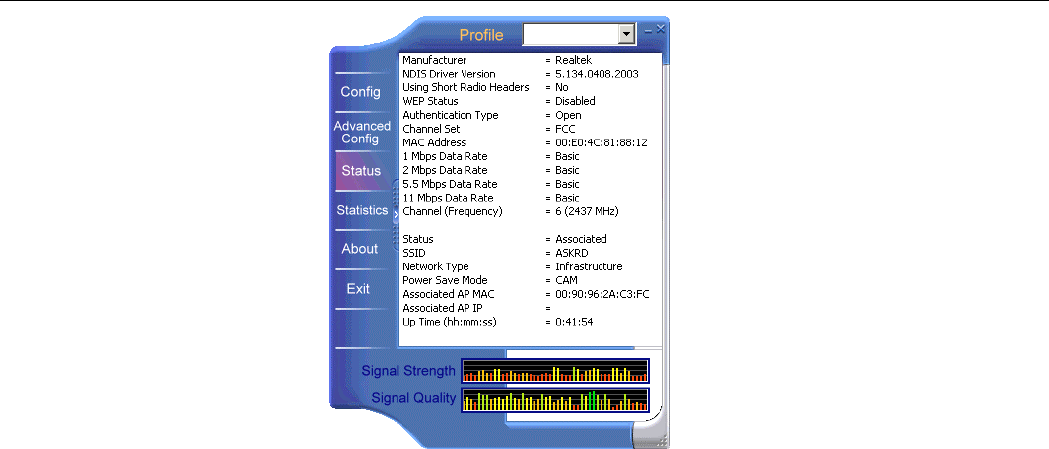
Status
This screen displays the detailed informatoin on your current wireless connecton.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
28
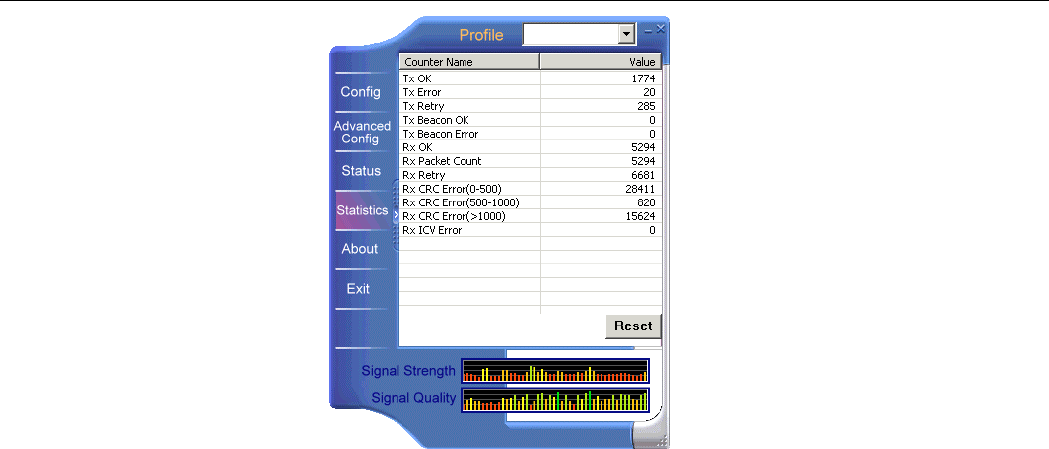
Statistics
This screen displays the statistics data on your current wireless connecton. You can
optionally click the Reset button to set the couter to zero.
Chapter 3 Using Wireless LAN Utility
29
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
30
About
The About screen displays information about the utility version.
31
Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility
Windows XP provides built-in Wireless Zero Configuration utility for wireless
configuration and monitoring. You can choose to configure your wireless network via either
the wireless LAN utility as described in preceding section, or to use the Windows XP
Wireless Zero Configuration utility.
This section only provides the essential instructions on using Windows XP wireless utility to
get your wireless network established. For more information please refer to Windows XP on-
line help.
Connecting to an Access Point or Wireless LAN Card
To connect to an existing Access Point/Wireless LAN Card, take out the following steps:
1. Right-click the Wireless Connection icon on the system tray and select View Available
Wireless Networks from the context menu.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
32
Note: Depending on whether your wireless network is established, the context menu may
come with different items.
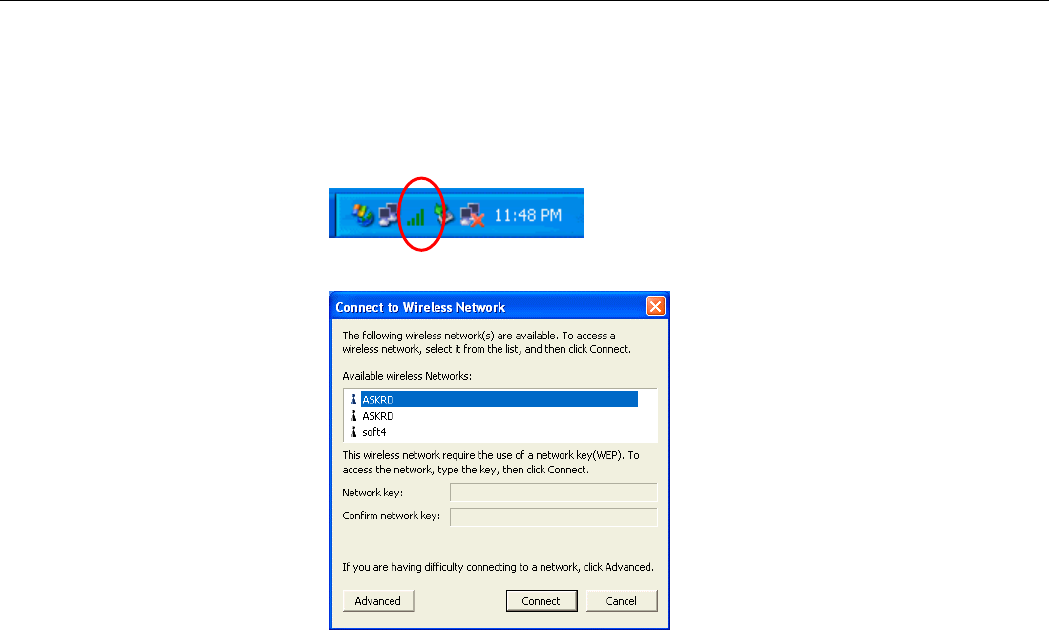
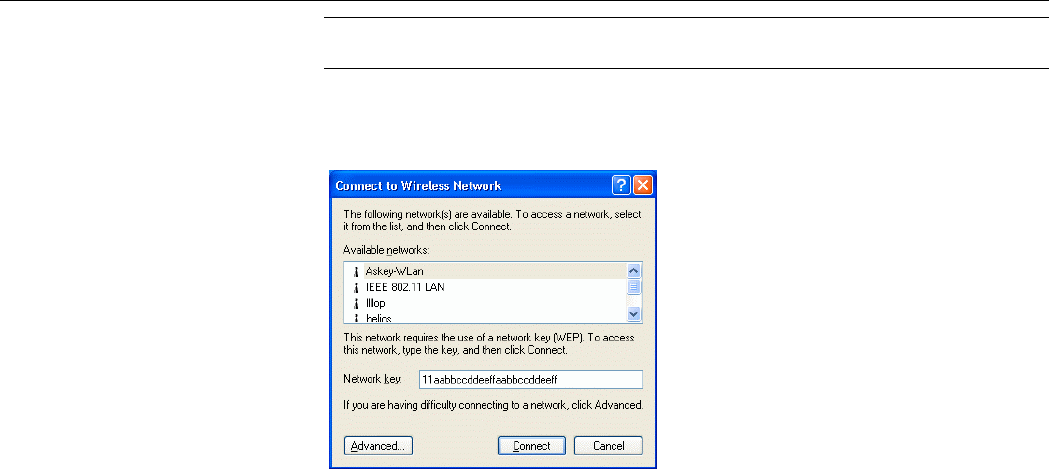
2. When the Connect to Wireless Network window pops up, you will see all the Access
Points or Wireless LAN Cards that are available in the air. Select the wireless network
you want to connect to .
Figure 5-1 Windows XP Configuration Utility-Connect to Wireless Network
3. If the target Access Point/Wireless LAN Card has been set with WEP key, you must
enter the same WEP key in the Network key field. Otherwise, leave it blank.

Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility
33
4. Click Connect, then you will join the target network and this dialog window will
disappear. When your wireless connection is established, the connection icon appears as
below:
Note: If the wireless connection can’t be established, double-click the connection icon and
then click Properties. Go to Authentication tab first to make sure that you use the correct
authentication type for the Wireless LAN Card. For more information, refer to
“Authentication” on page 39.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
34
Viewing Wireless Connection Status
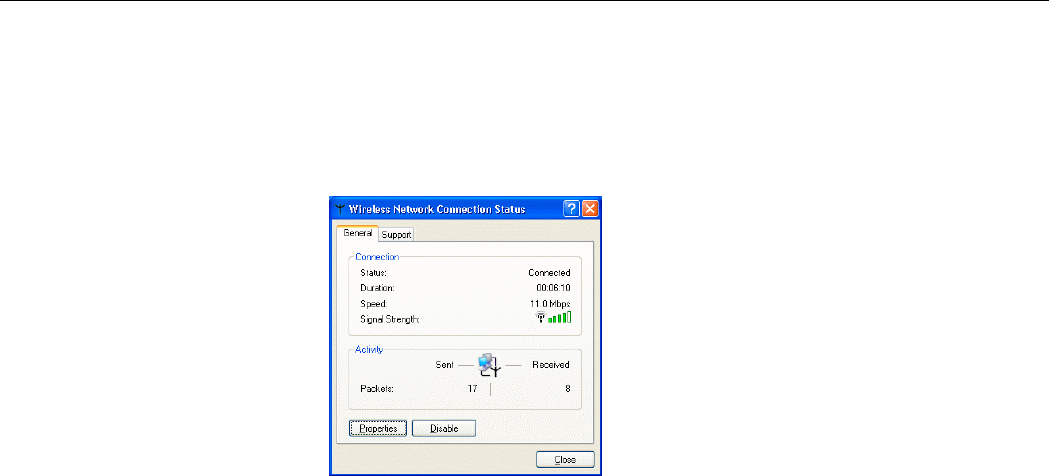
After you successfully connect to the Access Point or Wireless LAN Card, double-click the
icon in the system tray again. This will open the Wireless Network Connection Status
window where you can see the general data of the Wireless LAN Card, such as Status,
Duration, Speed, Signal Strength, etc.
Figure 5-2 Windows XP- Connection Status
Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility
35
Configuring Your Wireless Properties
To configure your wireless properties, open the Wireless Network Connection Status
window as described above, and then click the Properties button. This will open the Wireless
Network Connection Properties window which allows you to configure more detailed items
of the Wireless LAN Card. The following describes each tab of the properties window to help
you do more settings of the Wireless LAN Card.
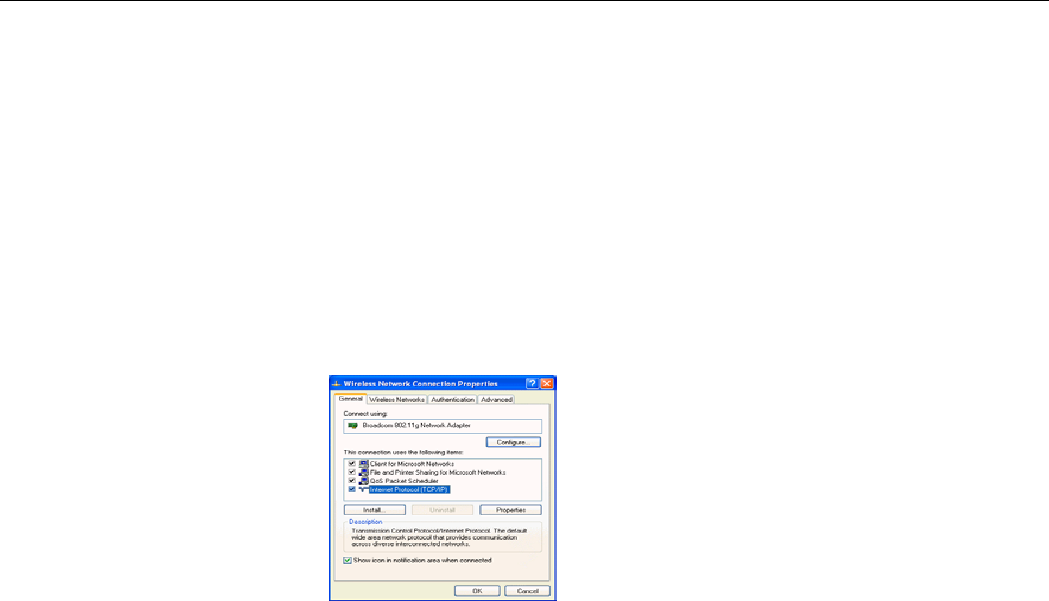
General
This tab allows you to specify the network methods to be used with your Wireless LAN Card.
The network policy depends on your wireless network. For TCP/IP protocol, you should
configure its properties as instructed by your network administrator. For more information on
TCP/IP setting, please refer to “Appendix B Setting Up TCP/IP” on page 51.
Figure 5-3 Windows XP Connection Properties -General
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
36
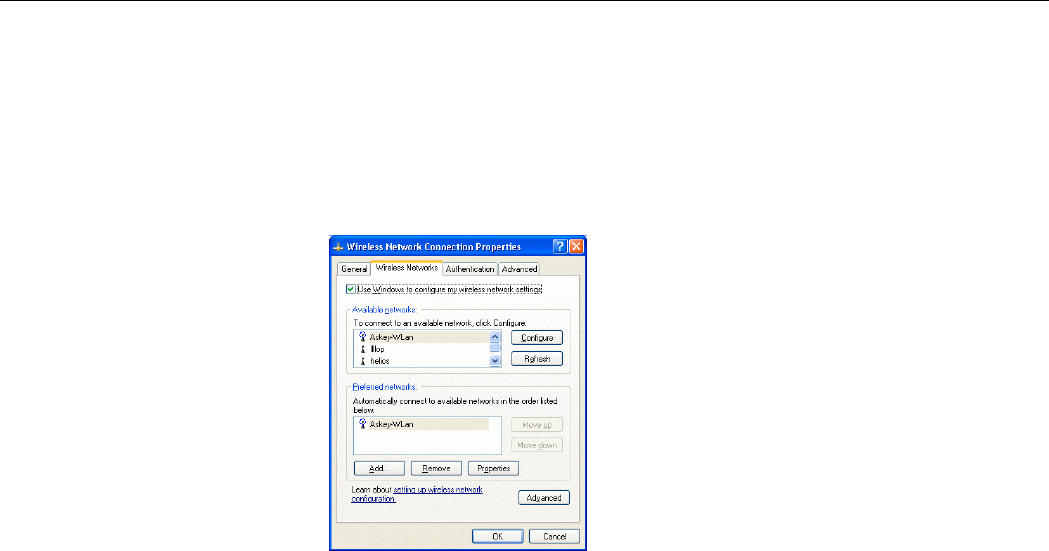
Wireless Networks
This tab contains two sections: Available networks and Preferred networks described as
below.
Under Available networks section, you can also see all the Access Points and Wireless LAN
Cards available in the air. Click Refresh to update the list of Access Points and Wireless LAN
Cards.
Figure 5-4 Windows XP Connection Properties-Wireless Networks
Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility
37
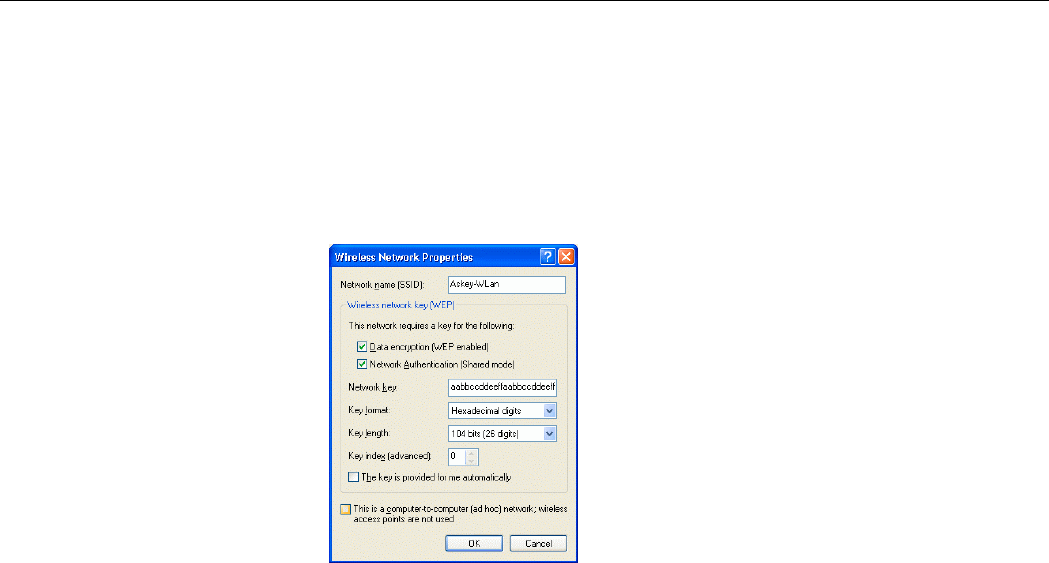
Under Preferred networks section, you can add any wireless networks that you wish to
connect to. To do this, just click Add to add more Access Points or Wireless LAN Cards to
the list.
After you click the Add button, the Wireless Network Properties window pops up. Type
your network name (SSID) and, if needed, the wireless network WEP settings. Once the
Access Point or Wireless LAN Card that you want to connect to has been set with WEP key,
you must type the same WEP key as the Access Point’s or Wireless LAN Card’s.
Figure 5-5 Windows XP-Add Preferred Networks

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
38
After you add several profiles into Preferred networks, you can change the order in which
connection attempts to preferred networks are made. Just select the target wireless network
and click Move up or Move down to move it to a desired position.
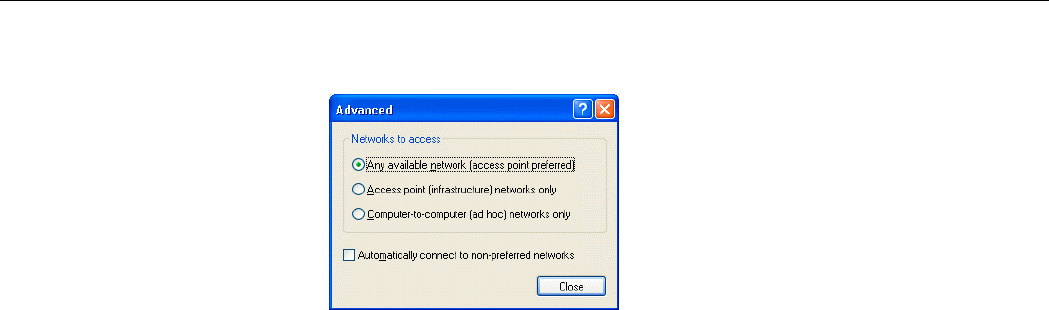
To Access Certain Wireless Network Only
If you just want to access certain wireless network type, click the Advanced button on the
Wireless Networks tab to open the Advanced window. You can choose to connect to the
following networks:
• Any available network (access point preferred)
• Access point (infrastructure)
• Computer-to-computer (Peer-to-Peer Group)
The default network type is Any available network (access point preferred). In this network
type, your device will connect to any Access Points or Wireless LAN Cards available in the
air but Access Point always demands higher connection attempt priority.
Chapter 5 Windows XP Wireless Zero Configuration Utility
39
Once you finish the advanced setting, your wireless station will then connect to your desired
network and the connected network will be listed under Available networks.
Figure 5-6 Windows XP Configuration Utility-Set up a Network to Aceess
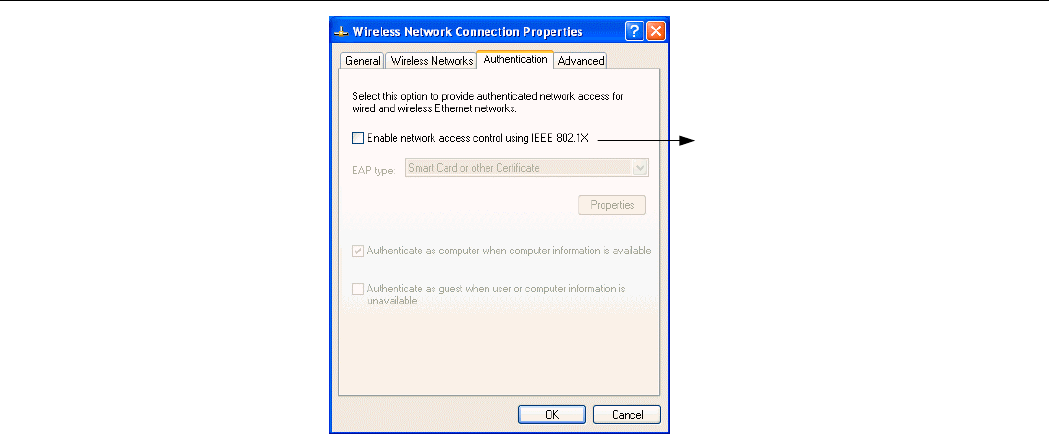
Authentication
This tab allows you to configure the authentication settings of your Wireless LAN Card. The
most important setting for the Wireless LAN Card is to disable Enable network access
control using IEEE802.1X to ensure successful connection between the Wireless LAN Cards
and Access Points or other Wireless LAN Cards. You must disable this function for any
reason. Otherwise, there may be some problems happening during connection. For other
settings, we recommend you keep the default settings to minimize the problems during
connection.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
40
Figure 5-7 Windows XP Connection Properties – Authentication
Make sure to disable Enable
network access control
using IEEE 802.1X.

41
Chapter 6 Uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card
Should you need to uninstall the Wireless LAN Card and application software for any reason,,
you should uninstall the associated software and then remove the hardware from your
computer. Please proceed as follows.
Uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card Software
Note: Before uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card software, please disable the utility by right-
clicking the utility tray icon and select Close from the context menu. The icon will disappear
to indicate that the utility is not in operation.
1. Close all programs that are currently running.
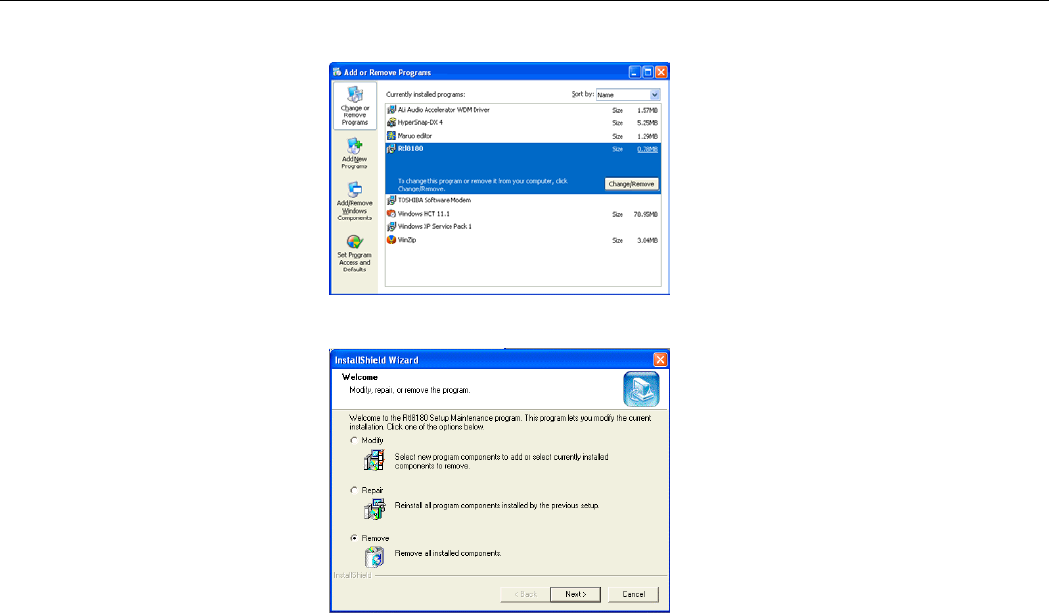
2. In Control Panel, double-click the Add or Remove Programs icon.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
42
3. Select Rtl8180 from the list and click Change/Remove.
4. Select Remove and click Next.
Chapter 6 Uninstalling the Wireless LAN Card
43
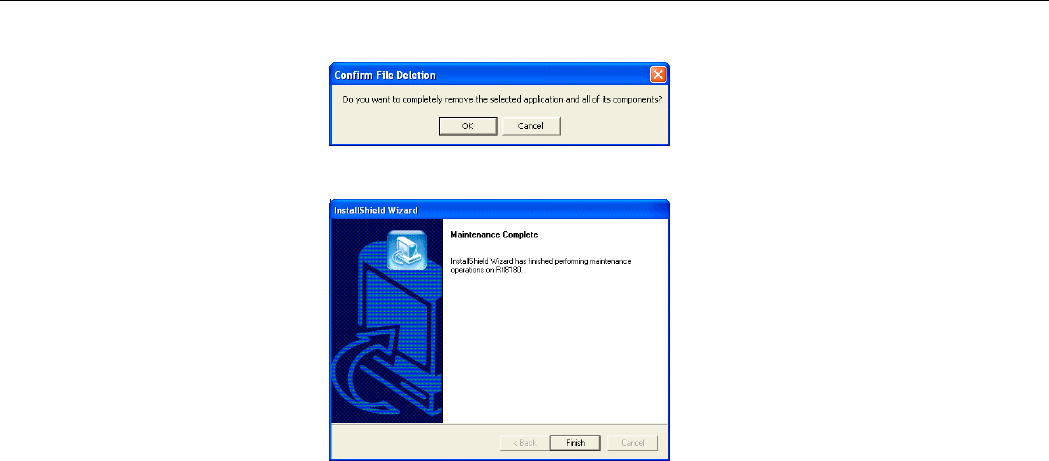
5. Click OK to proceed.
6. Click Finish to complete the removal.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
44
Removing the Wireless LAN Card (For CardBus Adapter)
To permanently remove the CardBus adapter from your computer, make sure that you have
removed the software before you proceed to remove the hardware.
The Wireless LAN Card complies with the PCMCIA standard that allows devices to be
inserted into and removed from the computer’s PCMCIA slot when the computer is powered
on. For a PCMCIA device, it is recommended that you follow the standard Windows
procedure for disconnecting a PCMCIA device from your computer. The following steps
assume a Windows 98 environment:
1. On the system tray, right-click the PCMCIA icon, and then click Adjust PC Card
Properties.
2. Select the Wireless LAN Card which you want to remove, click Stop.
3. When the message appears that tells you it is safe to remove device, click OK and remove
the Wireless LAN Card from the computer.
4. Click OK to exit the PC Card (PCMCIA) Properties window.
45
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Cannot Install under Windows 2000
When I installing the software under Windows 2000, I received the error message: “1608:
Unable to create InstallDriver instance” and the program stopped installing.
This error occurs when the Microsoft Network Client is not installed under Windows 2000.
To install this network component:
1. Go to Control Panel and double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
Right-click on the Local Area Connection, then select Properties.
2. Click Install > Client > Add > Client for Microsoft Networks > OK.
3. The Microsoft Network Client is now installed. Manually restart your computer to
enable the changes.
4. Then re-try to install the software as described in this manual.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
46
Radio Interference
You may be able to eliminate any interference by trying the following:
• Reseat the Wireless LAN Card.
• Increase the distance between the wireless computers and the device causing the
radio interference.
• Plug the computer equipped with the Wireless LAN Card into an outlet on a
different branch circuit from that used by the affecting device.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
• Keep the computer with the Wireless LAN Card away from the microwave oven
and large metal objects.
Card Not Detected
If the Wireless LAN Card is not detected by Windows, try the following:
• Make sure the Wireless LAN Card is properly inserted in the computer.
• For Cardbus wireless adapter, make sure you are using 32-bit Cardbus expansion
slot and the slot is working.
• Contact your dealer for additional testing if there is a hardware problem with the
Wireless LAN Card.

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
47
Cannot Connect to Another Wireless LAN Card
If you cannot make a connection to another Wireless LAN Card from your computer, it could
be due to one of the following reasons:
• Incorrect SSID. Make sure the SSID is the same for all computers that have a
Wireless LAN Card.
• Changes are not being recognized by your computer. Restart your computer.
• If in Ad-Hoc mode, make sure the Log on to Windows NT domain check box is
not selected in the Client for Microsoft Networks Properties dialog box in the
Network Configuration tab.
• Incorrect IP Address or Subnet Mask. Check these settings in the TCP/IP
Properties dialog box in the Network Configuration tab.
Poor Link Quality
If the Link Quality display stays in the poor range, it could be due to one of the following
reasons:
• Radio interference.
• Distance between Wireless LAN Card and the target Access Point or wireless client
is too far. Decrease the distance between the Wireless LAN Card and Access Point
or wireless client.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
48
Cannot Connect to Access Point
If you cannot make a connection to the Access Point, it could be due to one of the following
reasons:
• Make sure the Access Point have no physical connection problems.
• Make sure the SSID for the Wireless LAN Card is the same as the Access Point.
• Make sure the security settings are the same as that of Access Point.
49
Appendix A Limited Warranty
Wireless LAN Hardware
The seller warrants to the end user (“Customer”) that this hardware product will be free from
defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for 1 year from the date
of purchase from the seller or its authorized reseller. The seller’s sole obligation under this
express warranty shall be, at the seller’s option and expense, to repair the defective product or
part, deliver to Customer an equivalent product or part to replace the defective item, or if
neither of the two foregoing options is reasonably available, The seller may, in its sole
discretion, refund to the Customer the purchase price paid for the defective product. All
products that are replaced will become the property of the seller. Replacement products may
be new or reconditioned.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
50
Wireless LAN Software
The seller warrants to Customer that each software program licensed from it , except as noted
below, will perform in substantial conformance to its program specifications, for a period of 1
year from the date of purchase from the seller or its authorized reseller. The seller warrants the
media containing software against failure during the warranty period. No updates are provided.
The seller’s sole obligation under this express warranty shall be, at the seller’s option and
expense, to refund the purchase price paid by Customer for any defective software product, or
to replace any defective media with software which substantially conforms to applicable seller
published specifications. Customer assumes responsibility for the selection of the appropriate
application programs and associated reference materials. The seller makes no warranty or
representation that its software products will meet Customer’s requirements or work in
combination with any hardware or software applications products provided by third parties,
that the operation of the software products will be uninterrupted or error free, or that all
defects in the software products will be corrected. For any third party products listed in the
seller software product documentation or specifications as being compatible, the seller will
make reasonable efforts to provide compatibility, except where the non-compatibility is
caused by a defect in the third party’s product or from use of the software product not in
accordance with the seller’s published specifications or user manual.
51
Appendix B Setting Up TCP/IP
This section contains instructions for configuring the TCP/IP protocol of the Wireless LAN
Card. The IP address policy depends on your wireless network. You should configure your
TCP/IP protocol as instructed by your network administrator.
For Windows 98/ME
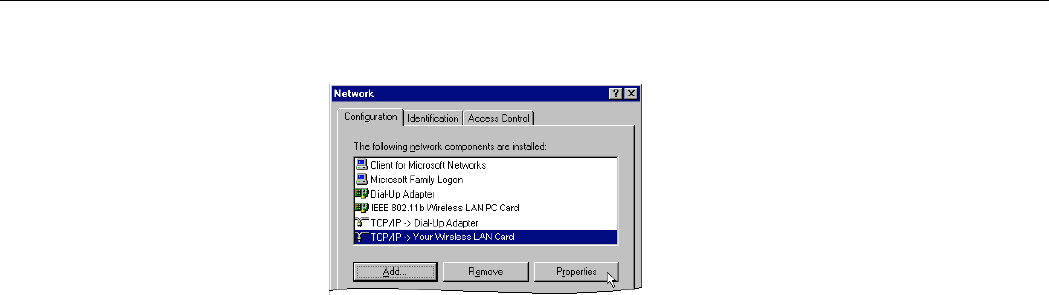
1. Double-click the Network icon on the Control Panel.
2. Click the Configuration tab of the Network dialog box.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
52
3. In the network components list, select the TCP/IP protocol of your Wireless LAN Card,
e.g., TCP/IP ->Realtek RTL8180 Wireless … and then click Properties.
4. On the IP Address tab, choose one of the methods as required:
Option A: Click Specify an IP address.
In the IP Address box, enter a valid four-component IP address, either a public or
private one as required.
In the Subnet Mask box, enter a valid four-component IP address.
Then select the Gateway tab and enter your gateway information.
Option B: Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
Then an IP address will be automatically assigned to your computer.

Appendix B Setting Up TCP/IP
53
5. Click OK to return to Network dialog box and click OK again to finish configuration. If
your TCP/IP properties have been modified, you will be prompted to restart your
computer. Click Yes to have new settings take effect.
11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
54
For Windows 2000/XP
1. Double-click Network Dial-up Connections (Windows 2000) or Network Connections
(Windows XP) on Control Panel, then Network Connections.
2. Right-click the Realtek RTL8180 Wireless … icon and click Properties.

Appendix B Setting Up TCP/IP
55
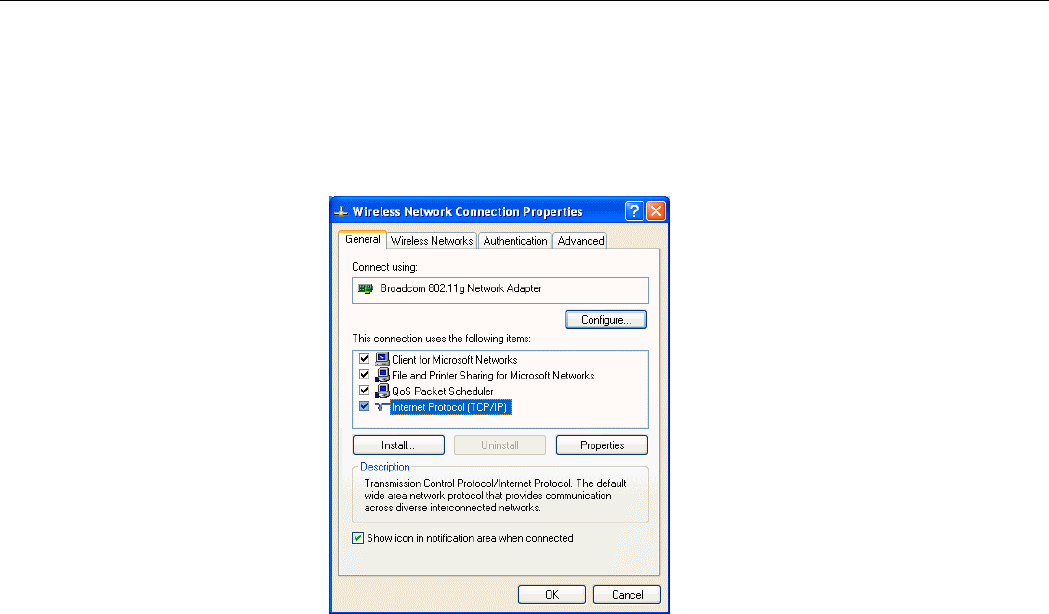
3. On the General tab, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click Properties.
Option A: Use fixed IP address.
Enable the Use the following IP Address option. Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask
and Default gateway. Then click OK.
Option B: Use dynamic IP address
Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
4. Close the Local Area Connection Properties window. For Windows 2000, if prompted,
click Yes to restart your computer.
57
Glossary
10BaseT An IEEE standard (802.3) for operating 10 Mbps Ethernet networks (LANs) with twisted pair
cabling and a wiring hub.
Access Point An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks. Access
Points combined with a distributed system support the creation of multiple radio cells that
enable roaming throughout a facility.
Ad-Hoc A network composed solely of stations within mutual communication range of each other (no
Access Point connected).
BSS Basic Service Set. A set of stations controlled by a single coordination function.
Channel A medium used to pass protocol data units that can be used simultaneously in the same volume
of space by other channels of the same physical layer, with an acceptably low frame error ratio
due to mutual interference.
ESS Extended Service Set. A set of one or more interconnected Basic Service Sets (BSSs) and
integrated Local Area Networks (LANs) can be configured as an Extended Service Set.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
58
Ethernet The most widely used medium access method, which is defined by the IEEE 802.3 standard.
Ethernet is normally a shared media LAN; i.e., all the devices on the network segment share
total bandwidth. Ethernet networks operate at 10Mbps using CSMA/CD to run over 10BaseT
cables.
Gateway A network component that acts as an entrance to another network.
IEEE 802.11 The IEEE 802.xx is a set of specifications for LANs from the Institute of Electrical and
Electronic Engineers (IEEE). Most wired networks conform to 802.3, the specification for
CSMA/CD-based Ethernet networks or 802.5, the specification for token ring networks. 802.11
defines the standard for wireless LANs encompassing three incompatible (non-interoperable)
technologies: Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS), Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
(DSSS), and Infrared. IEEE standards ensure interoperability between systems of the same
type.
Infrastructure A wireless network centered about an Access Point. In this environment, the Access Point not
only provides communication with the wired network but also mediates wireless network
traffic in the immediate neighborhood.
IP Internet Protocol. The standard protocol within TCP/IP that defines the basic unit of
information passed across an Internet connection by breaking down data messages into packets,
routing and transporting the packets over network connections, then reassembling the packets
at their destination. IP corresponds to the network layer in the ISO/OSI model.
IP Address An IP address is a 32-bit number that identifies each sender or receiver of information sent
across the Internet. An IP address has two parts: the identifier of a particular network on the
Internet and an identifier of the particular device (which can be a server or a workstation)
within that network.

Glossary
59
LAN Local Area Network. A communications network that serves users within a defined
geographical area. The benefits include the sharing of Internet access, files, and equipment,
such as printers and storage devices. Special network cabling (10BaseT) is often used to
connect the PCs together.
Radio
Frequency
RF, Terms: GHz, MHz, Hz —The international unit for measuring frequency is Hertz (Hz),
equivalent to the older unit of cycles per second. One megahertz (MHz) is one Million-Hertz.
One giga hertz (GHz) is one Billion-Hertz. The standard U.S. electrical power frequency is 60
Hz, the AM broadcast radio frequency band is 0.55–1.6 MHz, the FM broadcast radio
frequency band is 88–108 MHz, and wireless 802.11 LANs operate at 2.4GHz.
SSID Service Set ID. A group name shared by every member of a wireless network. Only client PCs
with the same SSID are allowed to establish a connection.
Subnet Mask A value that defines whether your computer communicates only within your LAN or
communicates outside of your LAN, where it is routed out to the rest of the Internet. A Subnet
Mask that has the same first three components (for example, 255.255.255.0) is the routing
pattern for a Class C address.
TCP Transmission Control Protocol. The standard transport level protocol that provides the full
duplex, stream service on which many applications’ protocols depend. TCP allows a process on
one machine to send a stream of data to a process on another. Software implementing TCP
usually resides in the operating system and uses the IP to transmit information across the
network.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
60
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy. The optional cryptographic confidentiality algorithm specified by
802.11. The algorithm is being used to provide data confidentiality that is subjectively
equivalent to the confidentiality of a wired LAN medium that does not employ cryptographic
techniques to enhance privacy..

Glossary
61
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.

11Mbps Wireless LAN Card User's Manual
62
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this
equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. End users must follow the specific operating
instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
This device complies with FCC RF Exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment, under 47 CFR 2.1093 paragraph (d)(2).

Glossary
63
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.